Is viewing ethanol content with VCDS possible, and what are the benefits? Yes, viewing ethanol content with VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System) is possible and offers significant benefits for tuning and diagnostics. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides expert remote support to help you navigate the complexities of accessing and interpreting this data, ensuring accurate adjustments and optimal vehicle performance. Our services include ECU programming, car coding assistance, and activating hidden features, all delivered with professional skill and precision.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Ethanol Content Monitoring with VCDS
- 2. Which Vehicles Support Ethanol Content Viewing via VCDS?
- 3. What VCDS Version Do I Need to View Ethanol Content?
- 4. How to Access Ethanol Content Data Using VCDS: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 5. Interpreting Ethanol Content Readings: What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting When Viewing Ethanol Content
- 7. Benefits of Knowing Your Vehicle’s Ethanol Content
- 8. How Ethanol Content Affects Engine Performance
- 9. Using Ethanol Content Data for Performance Tuning
- 10. Ethanol Sensors: Function and Maintenance
- 11. Potential Risks of Incorrect Ethanol Content Readings
- 12. How to Calibrate an Ethanol Sensor with VCDS
- 13. Alternative Tools for Monitoring Ethanol Content
- 14. Understanding Flex-Fuel Vehicle (FFV) Systems
- 15. Ethanol Content and Fuel Trim: Making Sense of the Relationship
- 16. Can You Adjust Ethanol Content Readings Using VCDS?
- 17. What Fault Codes Are Related to Ethanol Content?
- 18. How to Clear Ethanol-Related Fault Codes with VCDS
- 19. Upgrading Fuel System Components for High Ethanol Use
- 20. What Are the Safety Precautions When Working with Ethanol and VCDS?
- 21. The Future of Ethanol Monitoring in Automotive Technology
- 22. Real-World Examples of Ethanol Content Monitoring in Action
- 23. Resources for Learning More About Ethanol and VCDS
- 24. How to Log Ethanol Content Data with VCDS for Analysis
- 25. The Impact of Ethanol on Vehicle Warranties
- 26. Using VCDS to Check Fuel Injector Performance with Ethanol
- 27. Decoding Canbus Data for Ethanol Content on Unsupported Vehicles
- 28. How Remote Car Coding Services Can Help With Ethanol Monitoring
- 29. The Cost of Viewing Ethanol Content with VCDS vs. Alternatives
- 30. Is Viewing Ethanol Content VCDS Worth It?
1. Understanding Ethanol Content Monitoring with VCDS
What is the significance of monitoring ethanol content using VCDS? Monitoring ethanol content using VCDS is crucial for several reasons, especially in vehicles designed to run on flexible fuels (E85). It allows technicians and tuners to:
- Verify Fuel Composition: Ensure the actual ethanol percentage in the fuel matches the expected value.
- Optimize Engine Performance: Fine-tune engine parameters like ignition timing and fuel injection for optimal performance and efficiency based on the ethanol content.
- Diagnose Fuel System Issues: Identify potential problems with the fuel system, such as a faulty ethanol sensor or issues with fuel blending.
- Protect Against Engine Damage: Prevent potential engine damage caused by running an incorrect fuel mixture.
This data is critical for achieving the best possible performance and reliability from your vehicle.
2. Which Vehicles Support Ethanol Content Viewing via VCDS?
Which vehicle models are compatible with viewing ethanol content via VCDS? The ability to view ethanol content via VCDS is primarily available on vehicles equipped with a flex-fuel system (FFV), typically manufactured by Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT. Specific models that commonly support this feature include:
- Volkswagen: Golf, Jetta, Passat (especially models designated as FFV).
- Audi: A3, A4, A5, A6 (models with flex-fuel capability).
- Skoda: Octavia, Superb (flex-fuel variants).
- SEAT: Leon, Ibiza (flex-fuel variants).
It’s essential to verify the specific capabilities of your vehicle using VCDS or consult with a knowledgeable technician at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN.
3. What VCDS Version Do I Need to View Ethanol Content?
Which version of VCDS is required to access ethanol content data? To effectively view ethanol content, it’s recommended to use the latest version of VCDS from Ross-Tech. Newer versions include updated protocols and enhanced support for accessing advanced engine parameters, including ethanol content.
- Minimum Recommended Version: VCDS 11.11 or later is generally required, but using the most recent version ensures optimal compatibility and access to all available features.
- Software Updates: Regularly update your VCDS software to benefit from the latest improvements and vehicle support.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN always uses the latest VCDS software to provide accurate and reliable diagnostic and coding services.
4. How to Access Ethanol Content Data Using VCDS: A Step-by-Step Guide
What is the step-by-step procedure for accessing ethanol content data through VCDS? Accessing ethanol content data with VCDS involves a systematic process:
-
Connect VCDS: Connect the VCDS interface to your vehicle’s OBD-II port and start the VCDS software on your computer.
 Connecting VCDS Interface to Vehicle OBD-II Port
Connecting VCDS Interface to Vehicle OBD-II PortAlt Text: Connecting the VCDS interface to the OBD-II port in the vehicle for diagnostic and coding operations.
-
Select Control Module:
- Choose “Select Control Module” from the main menu.
- Select “01-Engine” to access the engine control unit (ECU).
-
Access Measuring Blocks:
- Click on “Measuring Blocks – 08.”
- Enter the appropriate group number or use the up/down arrows to find the measuring block that displays ethanol content. Common measuring blocks include:
- Ethanol Content: Look for a measuring block specifically labeled “Ethanol Content” or “Fuel Alcohol Percentage.”
- Fuel Trim Values: Check measuring blocks related to fuel trim, as these may indirectly indicate ethanol content adjustments.
-
View Data:
- Once you’ve located the correct measuring block, the ethanol content will be displayed as a percentage.
- Record the data for analysis or adjustment purposes.
-
Advanced Measuring Values:
- For more detailed information, use “Advanced Measuring Values” if available, allowing you to select specific parameters related to ethanol content.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can guide you through these steps remotely, ensuring you accurately access and interpret the data.
5. Interpreting Ethanol Content Readings: What Do the Numbers Mean?
How should ethanol content readings be interpreted, and what values are considered normal? Interpreting ethanol content readings is crucial for understanding your vehicle’s fuel composition and performance. Here’s what the numbers typically mean:
- 0% Ethanol: Indicates pure gasoline.
- Up to 10% Ethanol (E10): Standard gasoline blend in many regions.
- 15% Ethanol (E15): Approved for use in newer vehicles; check your vehicle’s compatibility.
- 51% to 83% Ethanol (E85): Designed for flex-fuel vehicles (FFV) and varies seasonally.
- Normal Values:
- For FFVs, the ethanol content should be within the range of 51% to 83% when using E85 fuel.
- When using regular gasoline (E10), the reading should be close to 0% to 10%.
Significant deviations from these values may indicate a problem with the fuel, the ethanol sensor, or the engine control system.
6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting When Viewing Ethanol Content
What common issues might arise when trying to view ethanol content, and how can they be resolved? Several issues can arise when attempting to view ethanol content with VCDS:
- Incompatible Vehicle: Not all vehicles support ethanol content monitoring.
- Solution: Verify that your vehicle is equipped with a flex-fuel system and that it is compatible with VCDS.
- Incorrect VCDS Version: Older versions may lack support for specific vehicle models or parameters.
- Solution: Update to the latest version of VCDS.
- Faulty Ethanol Sensor: A malfunctioning sensor can provide inaccurate readings.
- Solution: Check the sensor for damage or corrosion. Use VCDS to check for fault codes related to the ethanol sensor.
- Communication Problems: Issues with the VCDS interface or the vehicle’s communication bus.
- Solution: Ensure the VCDS interface is properly connected. Check the OBD-II port for damage. Try a different USB port or cable.
- Incorrect Measuring Block: Selecting the wrong measuring block can result in incorrect or no data.
- Solution: Consult the vehicle’s service manual or online resources to identify the correct measuring block for ethanol content.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers remote diagnostic services to help identify and resolve these issues efficiently.
7. Benefits of Knowing Your Vehicle’s Ethanol Content
What are the advantages of being able to monitor your vehicle’s ethanol content? Knowing your vehicle’s ethanol content offers several key benefits:
- Optimal Engine Tuning: Allows for precise adjustments to engine parameters, maximizing performance and fuel efficiency.
- Fuel Efficiency: Ensures the engine is running at its most efficient settings for the current fuel blend.
- Engine Protection: Prevents engine damage from running incorrect fuel mixtures.
- Diagnostic Insights: Helps identify potential issues with the fuel system or ethanol sensor.
- Flex-Fuel Vehicle Management: Essential for managing flex-fuel vehicles and ensuring they operate correctly on different fuel blends.
By understanding and monitoring ethanol content, you can optimize your vehicle’s performance and extend its lifespan.
8. How Ethanol Content Affects Engine Performance
How does the ethanol content of fuel impact the way an engine performs? The ethanol content in fuel significantly affects engine performance due to its unique properties:
- Higher Octane: Ethanol has a higher octane rating than gasoline, which can improve engine performance by allowing for more aggressive ignition timing.
- Leaner Air-Fuel Ratio: Engines require a richer (more fuel) air-fuel ratio when running on higher ethanol blends because ethanol contains less energy per unit volume compared to gasoline.
- Cooling Effect: Ethanol has a cooling effect on the intake charge, which can increase power output.
- Fuel System Compatibility: Higher ethanol concentrations may require upgraded fuel system components (e.g., fuel injectors, fuel pump) to handle the increased fuel flow and prevent corrosion.
Properly tuning the engine for the specific ethanol content ensures optimal performance and prevents potential damage.
9. Using Ethanol Content Data for Performance Tuning
How can ethanol content data be utilized to fine-tune a vehicle for enhanced performance? Ethanol content data is invaluable for performance tuning, enabling precise adjustments to optimize engine performance:
- Ignition Timing: Increase ignition timing when running higher ethanol blends to take advantage of its higher octane rating.
- Fuel Injection: Adjust fuel injection to maintain the correct air-fuel ratio, ensuring the engine receives the right amount of fuel for the ethanol content.
- Boost Levels: For turbocharged engines, ethanol’s cooling effect can allow for higher boost levels without risking detonation.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Use real-time ethanol content data to dynamically adjust engine parameters, ensuring optimal performance under varying fuel conditions.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers expert tuning support, helping you leverage ethanol content data to achieve maximum performance gains safely and effectively.
10. Ethanol Sensors: Function and Maintenance
What is the role of an ethanol sensor, and how should it be maintained to ensure accuracy? The ethanol sensor plays a critical role in flex-fuel vehicles, measuring the percentage of ethanol in the fuel and providing this information to the ECU. Proper maintenance is essential to ensure accurate readings:
- Function: The sensor uses a capacitance or optical method to determine the ethanol concentration in the fuel.
- Maintenance:
- Regular Inspections: Check the sensor for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Cleaning: Clean the sensor terminals to ensure good electrical contact.
- Testing: Use VCDS to monitor the sensor’s output and verify its accuracy.
- Replacement: Replace the sensor if it is faulty or providing inaccurate readings.
- Location: Typically located in the fuel line, near the fuel tank or fuel filter.
A properly functioning ethanol sensor is vital for accurate fuel adjustments and optimal engine performance.
11. Potential Risks of Incorrect Ethanol Content Readings
What risks are associated with inaccurate ethanol content readings, and how can they be avoided? Inaccurate ethanol content readings can lead to several potential risks:
- Engine Damage: Running an incorrect fuel mixture can cause detonation, pre-ignition, and other forms of engine damage.
- Reduced Performance: Incorrect fuel adjustments can result in reduced power, poor fuel economy, and rough running.
- Emissions Issues: Improper fuel combustion can lead to increased emissions and potential failure to meet emissions standards.
- Fuel System Problems: Over time, incorrect ethanol readings can contribute to fuel system corrosion and damage.
To avoid these risks:
- Regularly Verify Sensor Accuracy: Use VCDS to monitor the ethanol sensor’s output and ensure it is providing accurate readings.
- Proper Sensor Maintenance: Follow recommended maintenance procedures to keep the sensor in good working condition.
- Professional Tuning: Consult with a qualified tuner who can accurately interpret ethanol content data and make appropriate adjustments to the engine’s calibration.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides professional diagnostic and tuning services to help you avoid these risks and maintain optimal engine performance.
12. How to Calibrate an Ethanol Sensor with VCDS
Is it possible to calibrate an ethanol sensor using VCDS, and if so, how? While VCDS does not typically offer a direct “calibration” function for ethanol sensors, you can use it to verify the sensor’s accuracy and, in some cases, reset adaptation values that may affect its readings.
- Verification: Use VCDS to monitor the ethanol content reading while using a known fuel blend (e.g., pure gasoline or a specific E85 blend). Compare the reading to the actual ethanol content.
- Adaptation Reset: In some ECUs, you can reset fuel trim adaptation values, which may help the ECU relearn the correct ethanol content.
- Procedure:
- Connect VCDS to your vehicle.
- Select “01-Engine.”
- Go to “Adaptation – 10.”
- Look for channels related to fuel trim or ethanol content adaptation.
- Follow the instructions in VCDS to reset the adaptation values.
- Note: If the sensor consistently provides inaccurate readings, it may need to be replaced rather than calibrated.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can provide guidance on using VCDS to verify sensor accuracy and reset adaptation values.
13. Alternative Tools for Monitoring Ethanol Content
Besides VCDS, what other tools can be used to monitor ethanol content? While VCDS is a popular and effective tool, alternative options exist for monitoring ethanol content:
- Dedicated Ethanol Content Analyzers: These handheld devices directly measure the ethanol content of a fuel sample.
- OBD-II Scanners with Live Data: Many generic OBD-II scanners can display live data, including ethanol content, if the vehicle supports it.
- Smartphone Apps and Bluetooth Adapters: Some smartphone apps, paired with a Bluetooth OBD-II adapter, can access and display ethanol content data.
- Standalone Gauges: Dedicated gauges can be installed in the vehicle to continuously display ethanol content.
Each tool has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, accuracy, and ease of use.
14. Understanding Flex-Fuel Vehicle (FFV) Systems
How do flex-fuel vehicle (FFV) systems work, and how does ethanol content monitoring play a role? Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) are designed to run on a wide range of fuel mixtures, from pure gasoline to E85 (up to 85% ethanol). Here’s how these systems work:
- Ethanol Sensor: The ethanol sensor measures the ethanol content in the fuel.
- ECU Calibration: The ECU uses the ethanol content data to adjust engine parameters such as ignition timing, fuel injection, and air-fuel ratio.
- Fuel System Components: FFVs typically have upgraded fuel system components that are compatible with high ethanol concentrations.
- Monitoring Role: Ethanol content monitoring is essential for the ECU to make the correct adjustments and ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency, regardless of the fuel mixture.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN specializes in diagnosing and optimizing FFV systems, ensuring they operate correctly under all conditions.
15. Ethanol Content and Fuel Trim: Making Sense of the Relationship
What is the relationship between ethanol content and fuel trim, and how can VCDS help analyze it? Ethanol content and fuel trim are closely related, as the ECU adjusts fuel trim to compensate for the effects of ethanol on the air-fuel ratio. Here’s how to understand the relationship:
- Fuel Trim Basics: Fuel trim refers to the adjustments the ECU makes to the amount of fuel injected into the engine to maintain the correct air-fuel ratio.
- Short-Term Fuel Trim (STFT): Instantaneous adjustments made in response to current conditions.
- Long-Term Fuel Trim (LTFT): Learned adjustments based on STFT values over time.
- Ethanol Impact: When running on higher ethanol blends, the ECU will typically increase fuel trim to compensate for the leaner air-fuel ratio requirement.
- VCDS Analysis:
- Use VCDS to monitor both ethanol content and fuel trim values simultaneously.
- Analyze the relationship between the two to identify potential issues with the fuel system, ethanol sensor, or engine calibration.
- High positive fuel trim values (e.g., +10% or more) when running on E10 gasoline may indicate a problem.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides expert analysis of fuel trim data to help diagnose and resolve engine performance issues.
16. Can You Adjust Ethanol Content Readings Using VCDS?
Is it possible to manually adjust or override ethanol content readings using VCDS? No, VCDS does not allow you to manually adjust or override ethanol content readings. The ethanol sensor provides a real-time measurement of the fuel’s ethanol percentage, and the ECU uses this data to make necessary adjustments. Tampering with or manipulating this data can lead to serious engine damage.
- Focus on Accurate Data: Instead of trying to adjust the readings, focus on ensuring the sensor is functioning correctly and providing accurate data.
- Proper Tuning: Work with a qualified tuner to adjust engine parameters based on the actual ethanol content, rather than trying to manipulate the readings themselves.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN emphasizes safe and responsible tuning practices, ensuring that all adjustments are based on accurate data and sound engineering principles.
17. What Fault Codes Are Related to Ethanol Content?
Which diagnostic fault codes are commonly associated with issues related to ethanol content? Several fault codes can indicate problems related to ethanol content:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
- P0172: System Too Rich (Bank 1)
- P0175: System Too Rich (Bank 2)
- P0178: Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0179: Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit High Input
- P0180: Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Malfunction
- P0183: Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit High Input
These codes can indicate a faulty ethanol sensor, fuel system issues, or problems with the engine calibration. Use VCDS to read and interpret these codes, and consult with a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair.
18. How to Clear Ethanol-Related Fault Codes with VCDS
What is the procedure for clearing fault codes related to ethanol content using VCDS? Clearing fault codes related to ethanol content with VCDS involves the following steps:
- Connect VCDS: Connect the VCDS interface to your vehicle’s OBD-II port and start the VCDS software on your computer.
- Select Control Module: Choose “Select Control Module” from the main menu. Select “01-Engine” to access the engine control unit (ECU).
- Read Fault Codes: Click on “Fault Codes – 02.” This will display any stored fault codes in the ECU.
- Identify Ethanol-Related Codes: Look for fault codes related to the fuel composition sensor, fuel trim, or lean/rich conditions.
- Clear Fault Codes: Click on “Clear Codes – 05.” This will erase the stored fault codes from the ECU’s memory.
- Verify the Clear: After clearing the codes, restart the engine and recheck for any reappearing fault codes. If the codes return, it indicates an underlying issue that needs to be addressed.
Important: Clearing fault codes without addressing the underlying problem will only temporarily silence the warning light. The problem will likely recur, and the codes will return. Always diagnose and repair the root cause of the issue before clearing fault codes.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can assist you with diagnosing and resolving the underlying causes of ethanol-related fault codes, ensuring a permanent fix.
19. Upgrading Fuel System Components for High Ethanol Use
When is it necessary to upgrade fuel system components for vehicles running on high ethanol blends (e.g., E85)? Upgrading fuel system components is often necessary when running high ethanol blends (like E85) to ensure proper fuel delivery and prevent potential issues. Here are some key considerations:
- Fuel Injectors: Higher ethanol blends require more fuel to achieve the same air-fuel ratio as gasoline. Upgrading to larger fuel injectors is often necessary to provide sufficient fuel flow.
- Fuel Pump: A higher-capacity fuel pump may be needed to supply the increased fuel demand of high ethanol blends.
- Fuel Lines: Ethanol can be corrosive to some fuel lines. Upgrading to ethanol-compatible fuel lines is essential to prevent leaks and fuel system damage.
- Fuel Filter: A high-flow fuel filter can help maintain adequate fuel pressure and prevent clogging.
- ECU Tuning: The ECU must be properly tuned to account for the different fuel properties of high ethanol blends.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can advise on the appropriate fuel system upgrades for your vehicle and provide expert tuning services to optimize performance on high ethanol blends.
20. What Are the Safety Precautions When Working with Ethanol and VCDS?
What safety precautions should be observed when working with ethanol and VCDS? When working with ethanol and VCDS, it’s crucial to follow safety precautions to protect yourself and your vehicle:
- Ethanol Handling:
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling ethanol vapors.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from ethanol splashes.
- Gloves: Wear chemical-resistant gloves to prevent skin contact with ethanol.
- Fire Safety: Ethanol is flammable. Keep open flames and sources of ignition away from ethanol.
- Spills: Clean up any ethanol spills immediately using absorbent materials.
- VCDS Usage:
- Proper Connection: Ensure the VCDS interface is properly connected to the vehicle’s OBD-II port to avoid communication errors.
- Stable Power: Ensure your laptop has a stable power source to prevent interruptions during coding or programming.
- Software Updates: Keep your VCDS software up to date to benefit from the latest safety features and bug fixes.
- Follow Instructions: Carefully follow the instructions in the VCDS software and any accompanying documentation.
- Backup: Before making any changes to the vehicle’s coding or programming, create a backup of the original settings.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risks associated with working with ethanol and VCDS.
21. The Future of Ethanol Monitoring in Automotive Technology
How is ethanol monitoring likely to evolve in future automotive technology? The future of ethanol monitoring in automotive technology is likely to see several advancements:
- Improved Sensor Technology: More accurate and reliable ethanol sensors will provide more precise data to the ECU.
- Advanced Algorithms: Sophisticated algorithms in the ECU will use ethanol content data to optimize engine performance and emissions in real-time.
- Integration with Telematics: Ethanol content data may be integrated with telematics systems, allowing for remote monitoring and diagnostics.
- Expanded Flex-Fuel Capabilities: More vehicles may be designed with flex-fuel capabilities, allowing them to run on a wider range of ethanol blends.
- Focus on Sustainability: As the automotive industry moves towards more sustainable fuels, ethanol monitoring will play an increasingly important role in optimizing engine performance and reducing emissions.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN is committed to staying at the forefront of automotive technology, providing expert services for the latest ethanol monitoring systems.
22. Real-World Examples of Ethanol Content Monitoring in Action
Can you provide some real-world examples of how ethanol content monitoring is used in automotive applications? Real-world examples of ethanol content monitoring in action include:
- Performance Tuning: A tuner uses ethanol content data to optimize ignition timing and fuel injection for a turbocharged engine running on E85, resulting in increased horsepower and torque.
- Diagnostic Troubleshooting: A technician uses VCDS to identify a faulty ethanol sensor in a flex-fuel vehicle, resolving a drivability issue and preventing potential engine damage.
- Fuel Quality Verification: A race team uses an ethanol content analyzer to verify the ethanol content of their fuel before a race, ensuring they are running the correct fuel mixture for optimal performance.
- Fleet Management: A fleet manager uses telematics data to monitor the ethanol content of fuel used in their flex-fuel vehicles, ensuring they are taking advantage of the cost savings of E85 when available.
These examples illustrate the practical benefits of ethanol content monitoring in a variety of automotive applications.
23. Resources for Learning More About Ethanol and VCDS
Where can I find additional resources to expand my knowledge of ethanol and VCDS? To learn more about ethanol and VCDS, consider these resources:
- Ross-Tech Website: The official Ross-Tech website provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and support forums for VCDS.
- Automotive Forums: Online forums dedicated to automotive diagnostics and tuning often have discussions about ethanol and VCDS.
- Technical Manuals: Vehicle-specific technical manuals provide detailed information about the fuel system and ethanol sensor.
- Ethanol Industry Websites: Websites such as the Renewable Fuels Association (RFA) offer information about ethanol production, properties, and applications.
- Training Courses: Consider attending training courses on automotive diagnostics and tuning to gain hands-on experience with VCDS and ethanol-related topics.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN also provides educational resources and expert support to help you expand your knowledge of ethanol and VCDS.
24. How to Log Ethanol Content Data with VCDS for Analysis
What steps are involved in logging ethanol content data using VCDS for in-depth analysis? Logging ethanol content data with VCDS allows for in-depth analysis of engine performance and fuel system behavior. Follow these steps:
- Connect VCDS: Connect the VCDS interface to your vehicle’s OBD-II port and start the VCDS software.
- Select Control Module: Choose “Select Control Module” from the main menu. Select “01-Engine” to access the engine control unit (ECU).
- TDI Graph: Click on “TDI Graph” or “Data Logging” (depending on your VCDS version).
- Select Parameters: Choose the parameters you want to log, including ethanol content, fuel trim, RPM, and other relevant engine data.
- Start Logging: Click on “Start” to begin logging data.
- Drive Cycle: Perform a representative drive cycle that includes various driving conditions (e.g., idle, cruising, acceleration).
- Stop Logging: Click on “Stop” to end the data logging session.
- Save Data: Save the logged data to a file for analysis.
- Analyze Data: Use spreadsheet software or specialized data analysis tools to analyze the logged data and identify trends or anomalies.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can provide guidance on data logging and analysis, helping you extract valuable insights from your VCDS data.
25. The Impact of Ethanol on Vehicle Warranties
How might using high ethanol blends affect a vehicle’s warranty coverage? Using high ethanol blends can potentially affect a vehicle’s warranty coverage if the vehicle is not designed or approved for such fuels. Here are some considerations:
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or consult with the manufacturer to determine the approved fuel types and ethanol concentrations.
- Warranty Voidance: Using fuel that is not approved by the manufacturer may void the warranty on fuel system components or other related parts.
- Flex-Fuel Vehicles: Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) are designed to run on a wide range of ethanol blends, including E85, without affecting the warranty.
- Aftermarket Modifications: Aftermarket modifications to the fuel system or engine may also void the warranty.
It’s essential to understand your vehicle’s warranty coverage and fuel requirements before using high ethanol blends.
26. Using VCDS to Check Fuel Injector Performance with Ethanol
Can VCDS be used to assess fuel injector performance, particularly when using ethanol-blended fuels? Yes, VCDS can be a valuable tool for assessing fuel injector performance, especially when using ethanol-blended fuels. Here’s how:
- Monitoring Fuel Trim: As mentioned earlier, VCDS allows you to monitor short-term and long-term fuel trim values. Significant deviations from 0% can indicate injector issues. For instance, consistently high positive fuel trim values on one bank might suggest clogged or underperforming injectors on that side of the engine.
- Checking Injector Duty Cycle: VCDS can display the injector duty cycle, which is the percentage of time the injector is open during each engine cycle. Abnormally high duty cycles, especially at idle or low load, can indicate that the injectors are struggling to deliver enough fuel, potentially due to clogging or other issues.
- Measuring Injector Response Time: Some VCDS versions may offer the ability to measure injector response time. Slow or inconsistent response times can point to injector problems.
- Performing Output Tests: VCDS can perform output tests on individual injectors, allowing you to activate them and listen for proper operation. Unusual noises or a lack of response can indicate a faulty injector.
- Analyzing Misfire Data: VCDS can track misfires on a per-cylinder basis. Misfires that consistently occur on the same cylinder may be caused by a faulty injector.
By analyzing these parameters with VCDS, you can gain valuable insights into fuel injector performance and identify potential issues related to ethanol use.
27. Decoding Canbus Data for Ethanol Content on Unsupported Vehicles
Is it possible to decode Canbus data to view ethanol content on vehicles that don’t natively support it in VCDS? While challenging, decoding Canbus data to view ethanol content on unsupported vehicles is possible for advanced users with the right knowledge and tools. This involves:
-
Identifying the Relevant PID: You need to identify the specific Parameter ID (PID) that carries the ethanol content information on the vehicle’s Canbus network. This often requires extensive research, reverse engineering, and access to vehicle-specific technical documentation.
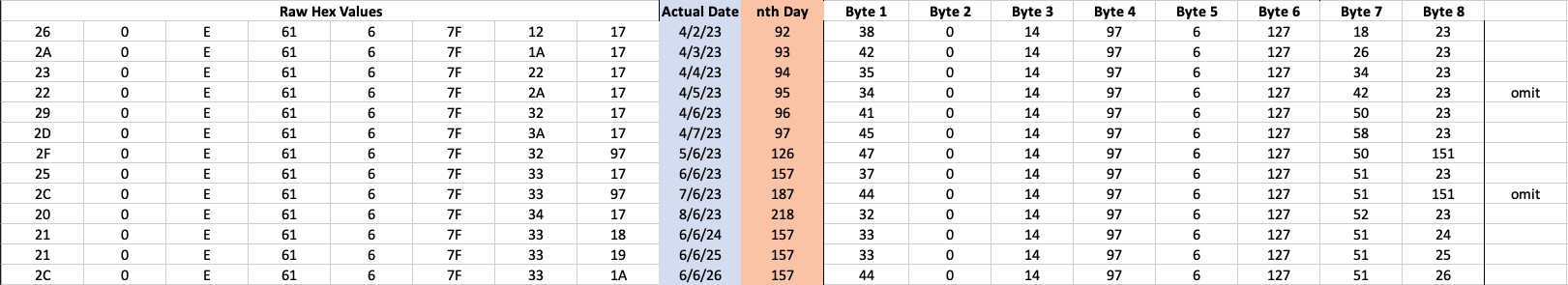 Ethanol Content Data Representation
Ethanol Content Data RepresentationAlt Text: Representation of ethanol content data on the CANbus network, showing values and byte correlations for different dates.
-
Canbus Sniffing: Use a Canbus sniffer tool to capture and analyze Canbus traffic while the vehicle is running. This allows you to observe the data being transmitted and identify potential PIDs related to ethanol content.
-
Data Interpretation: Once you’ve identified the relevant PID, you need to decode the data to extract the ethanol content value. This may involve understanding the data format, scaling factors, and other encoding schemes used by the vehicle manufacturer.
-
Custom Software/Scripts: You’ll likely need to develop custom software or scripts to process the Canbus data and display the ethanol content in a user-friendly format.
This process is complex and requires a deep understanding of Canbus networking, vehicle electronics, and data analysis techniques. It’s not recommended for beginners.
28. How Remote Car Coding Services Can Help With Ethanol Monitoring
In what ways can remote car coding services assist with ethanol monitoring and related issues? Remote car coding services, like those offered by CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, can be invaluable in addressing ethanol monitoring and related issues:
- Activating Hidden Features: In some cases, the ability to view ethanol content data may be a hidden feature that can be activated through coding. Remote coding services can help unlock this functionality.
- ECU Tuning and Calibration: Remote tuning specialists can adjust ECU parameters to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency based on ethanol content, ensuring the engine runs smoothly and efficiently on different fuel blends.
- Diagnostic Support: Remote diagnostic experts can use VCDS and other tools to diagnose ethanol-related issues, such as faulty sensors, fuel system problems, and incorrect ECU calibrations.
- Fault Code Clearing: Remote technicians can clear fault codes related to ethanol content and provide guidance on addressing the underlying causes.
- Software Updates: Remote coding services can help update the vehicle’s software to the latest version, which may include improved ethanol monitoring capabilities and bug fixes.
- Expert Advice: Remote coding specialists can provide expert advice and guidance on all aspects of ethanol monitoring, from selecting the right tools to interpreting data and troubleshooting problems.
By leveraging remote car coding services, you can access the expertise and tools needed to effectively monitor ethanol content and optimize your vehicle’s performance.
29. The Cost of Viewing Ethanol Content with VCDS vs. Alternatives
What are the cost considerations when choosing between VCDS and alternative methods for viewing ethanol content? The cost of viewing ethanol content varies depending on the method:
- VCDS:
- Initial Investment: Requires purchasing the VCDS interface, which can range from $200 to $400 or more, depending on the version and features.
- Software Updates: May require periodic software updates, which can incur additional costs.
- Long-Term Value: Offers comprehensive diagnostic and coding capabilities beyond ethanol monitoring, making it a valuable long-term investment for automotive enthusiasts and professionals.
- Dedicated Ethanol Content Analyzers:
- Cost: Can range from $100 to $300, depending on the brand and features.
- Limited Functionality: Primarily designed for measuring ethanol content and may not offer other diagnostic capabilities.
- OBD-II Scanners with Live Data:
- Cost: Can range from $50 to $200, depending on the features and brand.
- Variable Support: Ethanol content monitoring support may vary depending on the vehicle and scanner.
- Smartphone Apps and Bluetooth Adapters:
- Cost: Bluetooth adapters can range from $20 to $100, and apps may be free or require a subscription.
- Limited Reliability: Accuracy and reliability can vary depending on the app and adapter.
Consider your needs and budget when choosing the best method for viewing ethanol content. VCDS offers the most comprehensive capabilities, but dedicated analyzers or OBD-II scanners may be sufficient for basic ethanol monitoring.
30. Is Viewing Ethanol Content VCDS Worth It?
Ultimately, is investing in VCDS for viewing ethanol content worthwhile? Investing in VCDS for viewing ethanol content is worthwhile, especially if you:
- Own a Flex-Fuel Vehicle: Essential for monitoring and managing fuel mixtures.
- Performance Enthusiast: Enables precise tuning and optimization for ethanol-blended fuels.
- Automotive Professional: Provides comprehensive diagnostic and coding capabilities.
- Value Long-Term Investment: Offers ongoing value through software updates and support.
If you want to ensure accurate adjustments and optimal vehicle performance, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides expert remote support to help you navigate the complexities of accessing and interpreting this data.
Experiencing difficulty with coding or programming? Need immediate remote assistance? Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN now at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 100 Tech Innovation Dr, Suite 500, San Jose, CA 95110, United States for expert guidance.