Is diagnosing fuel pressure issues on your VW or Audi with VCDS proving difficult? At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of modern automotive systems and the need for expert guidance, offering remote support to help you accurately diagnose fuel pressure problems using VCDS measuring blocks. We provide real-time assistance for ECU programming, fault code clearing, and feature activation, ensuring efficient and precise solutions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding VCDS Measuring Blocks and Fuel Pressure Diagnostics
- 1.1 Why Fuel Pressure Monitoring is Important
- 1.2 Common Symptoms of Fuel Pressure Problems
- 2. Identifying Correct VCDS Measuring Blocks for Fuel Pressure
- 2.1 Ross-Tech Wiki and Other Resources
- 2.2 Using Advanced Measuring Blocks
- 3. Interpreting Fuel Pressure Data with VCDS
- 3.1 Understanding Normal Fuel Pressure Ranges
- 3.2 Diagnosing Common Fuel Pressure Issues
- 4. Practical Examples of Using VCDS for Fuel Pressure Diagnosis
- 4.1 Case Study: VW Jetta Hard Starting Issue
- 4.2 Identifying Fuel Pressure Regulator Problems
- 5. Addressing the Original Poster’s VCDS Challenges
- 5.1 Finding Fuel Rail Pressure on CJAA Engine
- 5.2 Interpreting “Absolute Pressure” Readings
- 6. Alternative Diagnostic Methods
- 6.1 Using a Mechanical Fuel Pressure Gauge
- 6.2 Performing a Fuel Pressure Leak-Down Test
- 7. Ensuring Accurate VCDS Readings
- 7.1 Verifying VCDS Software and Interface Cable
- 7.2 Checking for Fault Codes Related to Fuel System
- 8. When to Seek Professional Assistance
- 8.1 Benefits of Remote Diagnostic Support
- 8.2 CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Remote Support Partner
- 9. FAQs About VCDS and Fuel Pressure
- 9.1 Is it safe to perform fuel pressure diagnostics with VCDS myself?
- 9.2 What tools do I need for VCDS fuel pressure diagnosis?
- 9.3 How much does remote VCDS support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN cost?
- 9.4 Can VCDS activate the fuel pump for testing purposes?
- 9.5 What VW and Audi models are supported for VCDS fuel pressure diagnosis?
- 9.6 Are there any risks involved in car coding or ECU programming?
- 9.7 How can I permanently clear fault codes related to fuel pressure?
- 9.8 What is VIN coding and variant coding in the context of fuel systems?
- 9.9 How do CAN bus, MOST, FlexRay, and DoIP relate to fuel pressure diagnostics?
- 9.10 Where is CAR-CODING.EDU.VN located?
- 10. Take Action Now
1. Understanding VCDS Measuring Blocks and Fuel Pressure Diagnostics
What are VCDS measuring blocks and how can they aid in fuel pressure diagnosis? VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System) measuring blocks are real-time data displays within the VCDS software, allowing technicians to monitor various engine parameters, including fuel pressure. These blocks are crucial for diagnosing fuel-related issues, such as hard starting, poor performance, or fuel leaks. By interpreting the data from these blocks, you can identify whether the fuel system is functioning within specified parameters, pinpointing potential faults in components like the fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, or injectors. This diagnostic capability is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance and preventing costly repairs.
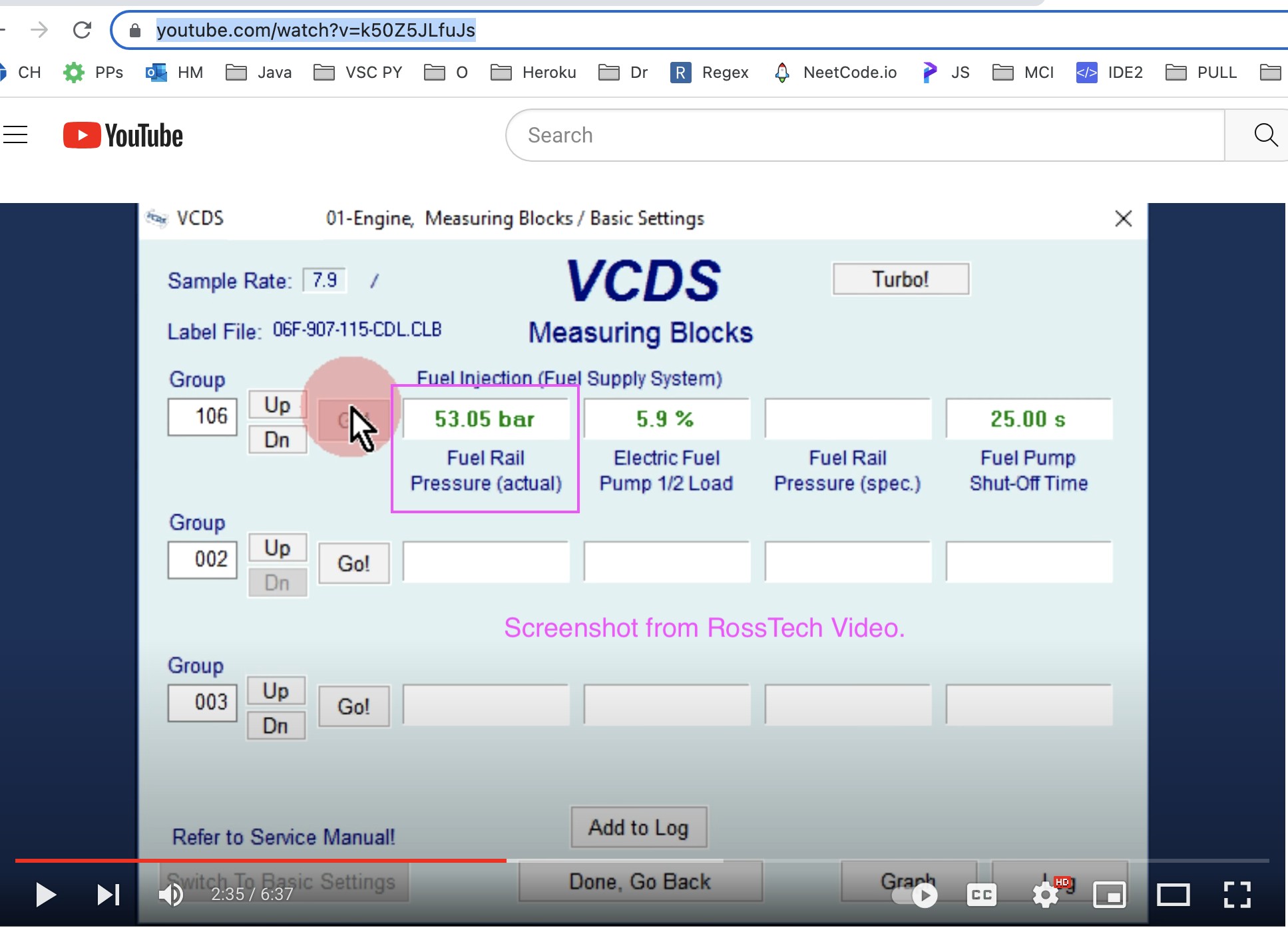 VCDS Measuring Blocks InterfaceIn addition to fuel pressure readings, VCDS can provide valuable data on other related parameters such as engine load, RPM, and injector duty cycle, giving a comprehensive view of the fuel system’s operation. This holistic approach enables technicians to diagnose complex issues that may not be immediately apparent from fuel pressure readings alone. For instance, a discrepancy between expected and actual fuel pressure under different engine loads can indicate a failing fuel pump or a clogged fuel filter. Understanding the interplay of these parameters is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective repairs.
VCDS Measuring Blocks InterfaceIn addition to fuel pressure readings, VCDS can provide valuable data on other related parameters such as engine load, RPM, and injector duty cycle, giving a comprehensive view of the fuel system’s operation. This holistic approach enables technicians to diagnose complex issues that may not be immediately apparent from fuel pressure readings alone. For instance, a discrepancy between expected and actual fuel pressure under different engine loads can indicate a failing fuel pump or a clogged fuel filter. Understanding the interplay of these parameters is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective repairs.
1.1 Why Fuel Pressure Monitoring is Important
Why is monitoring fuel pressure essential for maintaining vehicle performance? Monitoring fuel pressure is critical because it ensures the engine receives the correct amount of fuel for optimal combustion. Insufficient fuel pressure can lead to lean running conditions, causing performance issues such as hesitation, misfires, and reduced power. Conversely, excessive fuel pressure can result in overly rich conditions, leading to poor fuel economy, increased emissions, and potential damage to the catalytic converter. Regular monitoring of fuel pressure helps detect deviations from the normal range, allowing for timely intervention and preventing potential engine damage.
Fuel pressure directly impacts the air-fuel ratio, which is crucial for efficient combustion and emission control. A properly maintained fuel system delivers the precise amount of fuel needed for complete combustion, maximizing engine efficiency and minimizing harmful emissions. Deviations in fuel pressure can disrupt this balance, leading to incomplete combustion and increased levels of pollutants such as hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). By monitoring fuel pressure and addressing any issues promptly, you can ensure your vehicle operates cleanly and efficiently, meeting environmental standards and preserving engine health.
1.2 Common Symptoms of Fuel Pressure Problems
What are the typical symptoms that indicate fuel pressure issues in a vehicle? Common symptoms of fuel pressure problems include difficulty starting the engine, especially when cold; engine stalling shortly after starting; hesitation or stumbling during acceleration; poor fuel economy; and a noticeable decrease in engine power. These symptoms can arise from various issues, such as a failing fuel pump, a clogged fuel filter, a faulty fuel pressure regulator, or leaking injectors. Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent more severe engine damage and ensure timely repairs.
In addition to the above symptoms, fuel pressure problems can also manifest as rough idling, engine knocking, or a strong fuel odor. A failing fuel pump may struggle to maintain consistent fuel pressure, leading to erratic engine behavior and decreased performance. A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow, causing the engine to run lean and potentially overheat. A faulty fuel pressure regulator can cause either excessively high or low fuel pressure, disrupting the air-fuel mixture and affecting combustion efficiency. Leaking injectors can cause fuel to drip into the cylinders when the engine is off, leading to hard starting and rough running until the excess fuel is cleared.
2. Identifying Correct VCDS Measuring Blocks for Fuel Pressure
How do you identify the correct VCDS measuring blocks to read fuel pressure on your specific vehicle model? Identifying the correct VCDS measuring blocks for fuel pressure requires consulting the Ross-Tech Wiki, vehicle-specific repair manuals, or contacting experts at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for guidance. The location of fuel pressure data within VCDS can vary depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and engine control unit (ECU). Typically, fuel pressure readings can be found in Engine Control Module (ECM) measuring blocks, but the specific block numbers may differ.
Often, fuel pressure information can be located within measuring block groups such as 001, 106, 140, 230 or similar, however the availability of these groups can vary between models and ECU versions. If the standard measuring blocks do not display fuel pressure data, try using the “Advanced Measuring Blocks” function in VCDS, which allows you to search for specific parameters by name, such as “fuel pressure” or “rail pressure.” If you are unsure, it’s always best to consult a reliable source to ensure accurate diagnostics.
2.1 Ross-Tech Wiki and Other Resources
Where can you find reliable information on VCDS measuring blocks for specific vehicle models? The Ross-Tech Wiki is an excellent resource for finding information on VCDS measuring blocks, as it provides detailed guides and instructions for various VW, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT models. Vehicle-specific repair manuals, online forums dedicated to VCDS, and professional automotive diagnostic databases are also valuable sources. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers expert support and can guide you to the correct measuring blocks for your vehicle, ensuring accurate and efficient diagnostics.
Furthermore, online communities and forums dedicated to VCDS users can provide valuable insights and tips on locating fuel pressure data for specific vehicle models. These communities often share their experiences and knowledge, offering practical advice and troubleshooting tips. Additionally, professional automotive diagnostic databases such as Alldata and Mitchell OnDemand contain detailed information on vehicle-specific systems, including fuel pressure monitoring locations within VCDS. By leveraging these resources, you can enhance your diagnostic capabilities and accurately assess fuel system performance.
2.2 Using Advanced Measuring Blocks
How can you utilize the Advanced Measuring Blocks feature in VCDS to find fuel pressure data? The Advanced Measuring Blocks feature in VCDS allows you to search for specific parameters, such as fuel pressure, by name. To use this feature, connect VCDS to your vehicle, navigate to the Engine Control Module (ECM), and select “Advanced Measuring Blocks.” Enter “fuel pressure” or “rail pressure” in the search box, and VCDS will display any available measuring blocks containing that parameter. This method is particularly useful when the standard measuring blocks do not provide the desired data.
Once you have located the relevant measuring blocks, you can select them to display real-time data. Monitor the fuel pressure readings under various engine conditions, such as idle, acceleration, and deceleration, to assess the fuel system’s performance. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any deviations or anomalies. This process allows for a thorough evaluation of the fuel system, helping you pinpoint potential issues such as a failing fuel pump, a clogged fuel filter, or a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
3. Interpreting Fuel Pressure Data with VCDS
What does the fuel pressure data from VCDS measuring blocks tell you about your vehicle’s fuel system? The fuel pressure data from VCDS measuring blocks provides critical insights into the health and performance of your vehicle’s fuel system. By monitoring fuel pressure under various operating conditions, you can assess whether the fuel pump is delivering adequate pressure, the fuel pressure regulator is maintaining the correct pressure, and the injectors are functioning properly. Deviations from the specified pressure range can indicate potential issues such as a failing fuel pump, a clogged fuel filter, or a faulty regulator.
In addition to static fuel pressure readings, VCDS can also provide data on fuel pressure fluctuations during different engine conditions. For instance, a sudden drop in fuel pressure during acceleration can indicate a failing fuel pump that is unable to meet the increased fuel demand. Similarly, excessive fuel pressure at idle can point to a faulty fuel pressure regulator that is not properly relieving excess pressure. By analyzing these dynamic fuel pressure patterns, you can gain a deeper understanding of the fuel system’s behavior and identify potential problems that may not be apparent from static readings alone.
3.1 Understanding Normal Fuel Pressure Ranges
What are the normal fuel pressure ranges for different VW and Audi models, and how can you find this information? Normal fuel pressure ranges vary depending on the vehicle model and engine type. Typically, these values can be found in the vehicle’s repair manual or technical specifications. For example, many VW and Audi models with gasoline engines operate with a fuel pressure between 3 and 6 bar (43 to 87 PSI). Consulting the specific documentation for your vehicle is crucial for accurate diagnostics. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can provide this information as part of our remote support services.
Understanding the normal fuel pressure ranges is essential for interpreting VCDS data and identifying potential issues. Deviations from the specified range can indicate various problems, such as a failing fuel pump, a clogged fuel filter, or a faulty fuel pressure regulator. For instance, low fuel pressure can cause lean running conditions, leading to poor performance and potential engine damage. Conversely, high fuel pressure can result in rich running conditions, leading to poor fuel economy and increased emissions. By knowing the normal fuel pressure range for your vehicle, you can accurately assess the fuel system’s performance and address any issues promptly.
3.2 Diagnosing Common Fuel Pressure Issues
How can VCDS measuring blocks help diagnose common fuel pressure-related issues like a failing fuel pump or regulator? VCDS measuring blocks can help diagnose a failing fuel pump by monitoring the fuel pressure under load. A significant drop in pressure during acceleration indicates the pump is not providing sufficient fuel flow. For a fuel pressure regulator, VCDS can show if the pressure is consistently too high or too low, indicating a faulty regulator. Real-time data analysis with VCDS allows for precise identification of these issues.
Furthermore, VCDS can be used to monitor the fuel pump duty cycle, which provides insights into the pump’s operating efficiency. An excessively high duty cycle can indicate that the fuel pump is working harder than normal to maintain the required fuel pressure, suggesting a potential issue with the pump itself or a restriction in the fuel supply line. Similarly, VCDS can be used to activate the fuel pump and monitor the fuel pressure response. A slow or delayed pressure response can indicate a failing fuel pump or a leak in the fuel system. By combining fuel pressure readings with other relevant parameters, VCDS provides a comprehensive diagnostic tool for identifying fuel system problems.
4. Practical Examples of Using VCDS for Fuel Pressure Diagnosis
Can you provide some practical examples of how VCDS measuring blocks can be used in real-world fuel pressure diagnosis scenarios? Suppose a VW Jetta is experiencing hard starting and poor acceleration. Using VCDS, the technician monitors fuel pressure while cranking the engine and during acceleration. If the fuel pressure is below the specified range during cranking, it indicates a potential issue with the fuel pump or a fuel leak. During acceleration, a significant drop in fuel pressure further confirms the fuel pump’s inability to meet the engine’s demands.
Another example involves an Audi A4 with rough idling and poor fuel economy. The technician uses VCDS to monitor fuel pressure at idle and notices that it is consistently higher than the specified range. This suggests a faulty fuel pressure regulator that is not properly relieving excess pressure. By replacing the fuel pressure regulator, the technician resolves the issue and restores the engine’s smooth operation and fuel efficiency. These practical examples demonstrate the effectiveness of VCDS in diagnosing fuel pressure-related issues.
4.1 Case Study: VW Jetta Hard Starting Issue
How can VCDS measuring blocks help diagnose a hard starting issue in a VW Jetta, as described in the original post? In the case of the 2012 VW Jetta SportWagen TDI experiencing hard starting, VCDS measuring blocks can be used to monitor fuel rail pressure during the initial start attempt. By comparing the actual fuel rail pressure to the specified minimum pressure required for starting, the technician can determine if a pressure drop is indeed the cause of the hard starting issue. If the fuel pressure is below the threshold, it suggests a potential leak in the fuel system, a faulty fuel pressure regulator, or a failing fuel pump.
To further investigate, the technician can monitor the fuel pressure over time while the vehicle is sitting overnight. If the fuel pressure gradually decreases, it indicates a leak in the fuel system, possibly from a faulty injector or a leaking fuel line. Additionally, the technician can use VCDS to activate the fuel pump and monitor the fuel pressure build-up. A slow or delayed pressure build-up can indicate a failing fuel pump that is unable to prime the fuel system quickly enough for starting. By combining these diagnostic techniques, the technician can pinpoint the root cause of the hard starting issue and implement the appropriate repairs.
4.2 Identifying Fuel Pressure Regulator Problems
What steps can you take using VCDS to diagnose a faulty fuel pressure regulator? To diagnose a faulty fuel pressure regulator using VCDS, monitor the fuel pressure at idle and under various engine loads. If the fuel pressure is consistently higher or lower than the specified range, it indicates a potential issue with the regulator. Additionally, VCDS can be used to monitor the regulator’s duty cycle or control signal, if available. An erratic or abnormal signal can further confirm a faulty regulator.
Furthermore, you can perform a fuel pressure leak-down test using VCDS. After shutting off the engine, monitor the fuel pressure over time. A rapid decrease in fuel pressure indicates a leak in the fuel system, which could be caused by a faulty fuel pressure regulator, leaking injectors, or a leaking fuel line. By isolating the fuel pressure regulator and performing a manual pressure test, you can further confirm its functionality. If the regulator fails to maintain the specified pressure or exhibits erratic behavior, it should be replaced.
5. Addressing the Original Poster’s VCDS Challenges
How can the original poster’s specific challenges with VCDS measuring blocks be addressed to diagnose fuel pressure? The original poster’s difficulty in finding the correct measuring blocks for fuel pressure can be addressed by first verifying the accuracy of the VCDS software and interface cable. Ensure that the software is up-to-date and the cable is properly connected to the vehicle. Next, consult the Ross-Tech Wiki or vehicle-specific repair manuals for the correct measuring block locations for the 2012 VW Jetta SportWagen TDI with engine code CJAA.
If the standard measuring blocks do not display fuel pressure data, use the “Advanced Measuring Blocks” feature in VCDS and search for parameters such as “fuel pressure,” “rail pressure,” or “fuel rail pressure.” If these parameters are not available, it may indicate that the vehicle’s ECU does not directly measure fuel rail pressure or that the data is presented under a different name. In this case, consider monitoring other related parameters such as injector duty cycle, engine load, and RPM to infer fuel system performance. Alternatively, contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for expert assistance in locating the correct measuring blocks and interpreting the data.
5.1 Finding Fuel Rail Pressure on CJAA Engine
Where specifically can fuel rail pressure data be found on a 2012 VW Jetta SportWagen TDI with a CJAA engine using VCDS? On a 2012 VW Jetta SportWagen TDI with a CJAA engine, fuel rail pressure data may be found in VCDS measuring blocks within the Engine Control Module (ECM). Specifically, check measuring block groups such as 106, 140, 141, and 230, as these often contain fuel-related parameters. If the data is not available in these blocks, use the “Advanced Measuring Blocks” feature and search for “fuel pressure” or “rail pressure.”
It’s also possible that the fuel rail pressure data is presented under a different name or unit of measurement. For instance, the data may be displayed as “injection pressure” or in megapascals (MPa) instead of bar or PSI. If you are unable to locate the fuel rail pressure data, consult the Ross-Tech Wiki or vehicle-specific repair manuals for detailed instructions and diagrams. Additionally, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can provide remote support and guide you to the correct measuring blocks for your vehicle.
5.2 Interpreting “Absolute Pressure” Readings
How should the “Absolute Pressure” reading in Group 141 be interpreted in relation to fuel pressure diagnosis? The “Absolute Pressure” reading in VCDS Group 141 typically refers to the manifold absolute pressure (MAP), which measures the pressure in the intake manifold. While this reading is not directly related to fuel rail pressure, it can provide valuable information about the engine’s overall performance and air-fuel mixture. Monitoring the MAP sensor readings can help identify issues such as vacuum leaks, a faulty MAP sensor, or a clogged air filter, which can indirectly affect fuel pressure and engine performance.
To accurately diagnose fuel pressure-related issues, focus on finding the specific measuring blocks that display fuel rail pressure or injection pressure. If the “Absolute Pressure” reading is the only available pressure-related parameter, consider monitoring other relevant parameters such as injector duty cycle, engine load, and RPM to infer fuel system performance. Additionally, consult the Ross-Tech Wiki or vehicle-specific repair manuals for detailed instructions and diagrams. If you are still unable to locate the fuel rail pressure data, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can provide remote support and guide you to the correct measuring blocks for your vehicle.
6. Alternative Diagnostic Methods
What alternative diagnostic methods can be used if VCDS measuring blocks do not provide sufficient fuel pressure data? If VCDS measuring blocks do not provide sufficient fuel pressure data, alternative diagnostic methods include using a mechanical fuel pressure gauge to directly measure fuel pressure at the fuel rail. This method provides a reliable and accurate measurement, independent of the vehicle’s ECU and diagnostic software. Additionally, a fuel pressure leak-down test can be performed to check for leaks in the fuel system.
Another alternative is to use a professional-grade scan tool that offers more advanced diagnostic capabilities, such as bidirectional control and component testing. These scan tools can often access fuel pressure data that is not available through VCDS measuring blocks. Furthermore, consider consulting with experienced technicians or specialists who have expertise in diagnosing fuel system issues on VW and Audi vehicles. They may be able to provide valuable insights and guidance based on their experience.
6.1 Using a Mechanical Fuel Pressure Gauge
How do you use a mechanical fuel pressure gauge to manually measure fuel pressure? To use a mechanical fuel pressure gauge, first locate the fuel rail test port on your vehicle’s engine. This port is typically located on the fuel rail and is equipped with a Schrader valve. Attach the fuel pressure gauge to the test port, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection. Start the engine and observe the fuel pressure reading on the gauge. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the fuel pressure is within the normal range.
Monitor the fuel pressure under various engine conditions, such as idle, acceleration, and deceleration, to assess the fuel system’s performance. A significant drop in fuel pressure during acceleration indicates a potential issue with the fuel pump or a restriction in the fuel supply line. Similarly, excessive fuel pressure at idle can point to a faulty fuel pressure regulator. After completing the measurements, carefully disconnect the fuel pressure gauge and ensure that the test port is properly sealed.
6.2 Performing a Fuel Pressure Leak-Down Test
What is a fuel pressure leak-down test and how can it help diagnose fuel system problems? A fuel pressure leak-down test is a diagnostic procedure used to check for leaks in the fuel system. To perform this test, start the engine and allow it to reach operating temperature. Then, shut off the engine and immediately monitor the fuel pressure using a fuel pressure gauge or VCDS measuring blocks. Observe the fuel pressure over time and note any decrease in pressure.
A rapid decrease in fuel pressure indicates a leak in the fuel system, which could be caused by a faulty fuel pressure regulator, leaking injectors, or a leaking fuel line. To isolate the source of the leak, you can perform additional tests such as disconnecting the fuel pressure regulator or individually testing the injectors. By identifying and addressing the leak, you can restore the fuel system’s integrity and resolve issues such as hard starting, poor performance, and fuel economy problems.
7. Ensuring Accurate VCDS Readings
What steps can be taken to ensure the accuracy of VCDS readings during fuel pressure diagnosis? To ensure the accuracy of VCDS readings during fuel pressure diagnosis, first verify that the VCDS software is up-to-date and compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Use a genuine Ross-Tech interface cable to establish a reliable connection between the vehicle and the diagnostic computer. Check the cable for any signs of damage or wear, and ensure that it is properly connected to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
Before starting the diagnostic procedure, perform a full scan of the vehicle’s control modules to identify any fault codes that may be related to the fuel system. Clear any irrelevant fault codes to avoid confusion. During the diagnostic process, monitor the VCDS readings in real-time and compare them to the manufacturer’s specifications. If you notice any discrepancies or anomalies, double-check the connections and software settings. Additionally, consider consulting with experienced technicians or specialists who have expertise in using VCDS for fuel pressure diagnosis.
7.1 Verifying VCDS Software and Interface Cable
Why is it important to verify the VCDS software and interface cable before performing fuel pressure diagnosis? It is crucial to verify the VCDS software and interface cable before performing fuel pressure diagnosis because outdated or incompatible software and faulty cables can lead to inaccurate readings and unreliable diagnostic results. Using the latest version of the VCDS software ensures that you have access to the most up-to-date measuring blocks, diagnostic functions, and vehicle-specific information.
A genuine Ross-Tech interface cable provides a reliable and stable connection between the vehicle and the diagnostic computer, minimizing the risk of data corruption or communication errors. Check the cable for any signs of damage or wear, such as frayed wires or bent connectors. Ensure that the cable is properly connected to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and that the software recognizes the cable. By verifying the VCDS software and interface cable, you can ensure the accuracy and reliability of your diagnostic efforts.
7.2 Checking for Fault Codes Related to Fuel System
How can checking for fault codes related to the fuel system improve the accuracy of fuel pressure diagnosis? Checking for fault codes related to the fuel system can significantly improve the accuracy of fuel pressure diagnosis by providing valuable clues about potential issues. Fault codes can indicate problems such as a failing fuel pump, a faulty fuel pressure regulator, leaking injectors, or a clogged fuel filter. By identifying and addressing these fault codes, you can narrow down the potential causes of fuel pressure problems and focus your diagnostic efforts on the most likely culprits.
Before performing any fuel pressure measurements, perform a full scan of the vehicle’s control modules to identify any stored fault codes. Pay close attention to codes related to the fuel system, such as those indicating low fuel pressure, high fuel pressure, or injector circuit malfunctions. Research the fault codes to understand their potential causes and implications. Clear any irrelevant fault codes to avoid confusion. By using fault codes as a starting point, you can streamline the diagnostic process and improve the accuracy of your fuel pressure diagnosis.
8. When to Seek Professional Assistance
When should you seek professional assistance from a specialist like CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for fuel pressure diagnosis? You should seek professional assistance from a specialist like CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for fuel pressure diagnosis when you are unable to locate the correct VCDS measuring blocks, are unsure how to interpret the data, or suspect a complex fuel system issue that requires advanced diagnostic skills and equipment. Additionally, if you have attempted to diagnose the problem yourself but have been unsuccessful, it is best to consult with a professional to avoid potential damage to your vehicle.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers remote support and expert guidance for fuel pressure diagnosis, providing you with access to experienced technicians and specialized diagnostic tools. Our team can help you identify the correct VCDS measuring blocks, interpret the data, and develop a comprehensive diagnostic plan. We can also provide remote coding and programming services to address any ECU-related issues that may be contributing to the fuel pressure problem. By seeking professional assistance, you can ensure that your vehicle is properly diagnosed and repaired, minimizing downtime and preventing costly repairs.
8.1 Benefits of Remote Diagnostic Support
What are the benefits of using remote diagnostic support for fuel pressure troubleshooting? The benefits of using remote diagnostic support for fuel pressure troubleshooting include access to expert technicians, cost savings, convenience, and faster turnaround times. Remote support allows you to connect with experienced professionals who have specialized knowledge and skills in diagnosing fuel system issues on VW and Audi vehicles.
Remote diagnostic support eliminates the need to transport your vehicle to a repair shop, saving you time and money. You can perform the diagnostic procedures yourself, with guidance from a remote technician, using your own VCDS software and equipment. This allows you to troubleshoot the problem at your own pace and on your own schedule. Remote support also provides faster turnaround times, as you can often receive immediate assistance and resolve the issue without waiting for an appointment at a repair shop. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers comprehensive remote diagnostic support services, providing you with the expertise and resources you need to accurately diagnose and repair fuel pressure problems.
8.2 CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Remote Support Partner
How can CAR-CODING.EDU.VN assist with fuel pressure diagnosis and related car coding needs? CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can assist with fuel pressure diagnosis and related car coding needs by providing expert remote support, guiding you to the correct VCDS measuring blocks, interpreting data, and offering solutions for complex fuel system issues. We specialize in VW and Audi vehicles, offering in-depth knowledge of their fuel systems and diagnostic procedures.
Our team can also assist with car coding needs, such as ECU programming, fault code clearing, and feature activation. We use state-of-the-art diagnostic tools and remote access technology to connect to your vehicle and perform coding and programming tasks remotely. This allows you to enhance your vehicle’s performance, customize its features, and resolve any ECU-related issues that may be contributing to fuel pressure problems. With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN as your remote support partner, you can ensure that your vehicle receives the highest quality diagnostic and coding services.
9. FAQs About VCDS and Fuel Pressure
Here are some frequently asked questions about VCDS and fuel pressure diagnosis:
9.1 Is it safe to perform fuel pressure diagnostics with VCDS myself?
Is it generally safe for vehicle owners to perform fuel pressure diagnostics using VCDS on their own? Performing fuel pressure diagnostics with VCDS is generally safe for vehicle owners who have a good understanding of automotive systems and diagnostic procedures. However, it is important to exercise caution and follow safety guidelines to avoid potential hazards. Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the fuel system. Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid exposure to fuel vapors. Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect your eyes and skin.
If you are not comfortable performing fuel pressure diagnostics yourself, it is best to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician. Improper diagnostic procedures can lead to fuel leaks, fire hazards, and damage to your vehicle. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers remote support and expert guidance for fuel pressure diagnosis, providing you with the expertise and resources you need to safely and accurately troubleshoot fuel system issues.
9.2 What tools do I need for VCDS fuel pressure diagnosis?
What specific tools are required to effectively perform fuel pressure diagnosis using VCDS? To effectively perform fuel pressure diagnosis using VCDS, you will need a VCDS software license, a compatible Ross-Tech interface cable, a laptop computer with a stable internet connection, and a basic set of hand tools. The VCDS software and interface cable are essential for accessing the vehicle’s diagnostic data and performing various diagnostic functions.
A laptop computer is needed to run the VCDS software and connect to the vehicle. A stable internet connection is required for remote support and accessing online resources. A basic set of hand tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and screwdrivers, may be needed to access the fuel system components and perform basic repairs. Additionally, a mechanical fuel pressure gauge may be useful for verifying the accuracy of VCDS readings and performing fuel pressure leak-down tests.
9.3 How much does remote VCDS support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN cost?
What is the typical cost associated with obtaining remote VCDS support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for fuel pressure-related issues? The cost of remote VCDS support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for fuel pressure-related issues varies depending on the complexity of the problem and the amount of time required to resolve it. We offer flexible pricing options, including hourly rates and fixed-price packages. Contact us for a personalized quote based on your specific needs.
We strive to provide cost-effective solutions for fuel pressure diagnosis and related car coding needs. Our remote support services can save you time and money compared to traditional repair shop visits. We offer transparent pricing and upfront estimates, so you know exactly what to expect before committing to our services. With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, you can receive expert diagnostic support at an affordable price.
9.4 Can VCDS activate the fuel pump for testing purposes?
Is it possible to utilize VCDS to directly activate the fuel pump in order to conduct testing procedures? Yes, VCDS can be used to activate the fuel pump for testing purposes on many VW and Audi vehicles. This function allows you to manually control the fuel pump and observe its performance, such as its ability to build and maintain fuel pressure. Activating the fuel pump with VCDS can be helpful in diagnosing fuel pump issues, such as a failing pump or a clogged fuel filter.
To activate the fuel pump with VCDS, navigate to the Engine Control Module (ECM) and select “Output Tests” or “Actuator Tests.” Look for an option to activate the fuel pump. Follow the on-screen instructions to initiate the test. Monitor the fuel pressure using VCDS measuring blocks or a mechanical fuel pressure gauge while the fuel pump is activated. If the fuel pump fails to build or maintain adequate fuel pressure, it may indicate a problem with the pump itself or the fuel supply line.
9.5 What VW and Audi models are supported for VCDS fuel pressure diagnosis?
Which specific Volkswagen and Audi models are compatible with VCDS for the purpose of diagnosing fuel pressure issues? VCDS supports a wide range of VW and Audi models for fuel pressure diagnosis, including the VW Jetta, Golf, Passat, Tiguan, and Touareg, as well as the Audi A3, A4, A6, Q5, and Q7. The specific models and years supported may vary depending on the VCDS software version and interface cable.
To determine if your vehicle is supported, consult the Ross-Tech website or the VCDS software documentation. You can also contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for assistance in determining compatibility. We have extensive experience in diagnosing fuel pressure issues on VW and Audi vehicles and can provide expert guidance and support. Whether you have a classic model or a late-model vehicle, we can help you troubleshoot fuel pressure problems using VCDS.
9.6 Are there any risks involved in car coding or ECU programming?
What potential risks should be considered before undertaking car coding or ECU programming procedures? Yes, there are risks involved in car coding or ECU programming, especially if performed incorrectly or without proper knowledge. Incorrect coding or programming can lead to various problems, such as engine damage, electrical malfunctions, and loss of vehicle functionality. It is important to exercise caution and follow best practices to minimize these risks.
Before performing any car coding or ECU programming, make sure to back up the original coding data. This will allow you to revert to the original settings if something goes wrong. Use a reliable VCDS software and interface cable. Follow the instructions carefully and double-check your work. If you are not comfortable performing car coding or ECU programming yourself, it is best to seek professional assistance from a qualified technician. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers remote coding and programming services, providing you with the expertise and resources you need to safely and effectively modify your vehicle’s ECU.
9.7 How can I permanently clear fault codes related to fuel pressure?
What steps are necessary to permanently clear fault codes associated with fuel pressure irregularities using VCDS? To permanently clear fault codes related to fuel pressure using VCDS, you must first address the underlying issue that is causing the fault codes. Simply clearing the fault codes without fixing the problem will only result in the codes reappearing. Diagnose the fuel system to identify the root cause of the fuel pressure irregularities.
Once you have fixed the problem, use VCDS to clear the fault codes. To do this, connect VCDS to your vehicle, navigate to the Engine Control Module (ECM), and select “Fault Codes – 02.” Click the “Clear Codes – 05” button to erase the fault codes. After clearing the fault codes, drive the vehicle under various conditions to ensure that the codes do not reappear. Monitor the fuel pressure using VCDS measuring blocks to verify that the fuel system is functioning properly.
9.8 What is VIN coding and variant coding in the context of fuel systems?
Could you explain the concepts of VIN coding and variant coding and their relevance to fuel system diagnostics? VIN coding and variant coding are important concepts in the context of fuel systems and ECU programming. VIN coding refers to the process of programming the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) into the ECU. This is necessary when replacing an ECU to ensure that the new ECU is properly matched to the vehicle.
Variant coding refers to the process of configuring the ECU to match the specific options and features of the vehicle. This may involve enabling or disabling certain functions, such as fuel pump control, injector settings, or fuel pressure regulation. Incorrect VIN coding or variant coding can lead to various problems, such as fuel system malfunctions, engine damage, and loss of vehicle functionality. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers remote coding and programming services to ensure that your vehicle’s ECU is properly configured.
9.9 How do CAN bus, MOST, FlexRay, and DoIP relate to fuel pressure diagnostics?
How do communication protocols like CAN bus, MOST, FlexRay, and DoIP play a role in fuel pressure diagnostics? CAN bus (Controller Area Network), MOST (Media Oriented Systems Transport), FlexRay, and DoIP (Diagnostics over Internet Protocol) are communication protocols used in modern vehicles to facilitate communication between various electronic control units (ECUs). These protocols play a crucial role in fuel pressure diagnostics by allowing diagnostic tools like VCDS to access and interpret data from the fuel system components.
CAN bus is the most common communication protocol used in automotive applications. It allows the ECUs to communicate with each other and share data. MOST is a high-speed communication protocol used for multimedia applications. FlexRay is a high-speed, fault-tolerant communication protocol used for safety-critical applications. DoIP is a communication protocol that allows diagnostic tools to access ECUs over the internet. By understanding these communication protocols, technicians can better diagnose and troubleshoot fuel pressure issues.
9.10 Where is CAR-CODING.EDU.VN located?
Where are CAR-CODING.EDU.VN’s support facilities physically located? Our office is at 100 Tech Innovation Dr, Suite 500, San Jose, CA 95110, United States. However, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides remote support globally. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for assistance.
10. Take Action Now
Are you struggling to diagnose fuel pressure issues with your VW or Audi? Don’t waste time and risk further damage to your vehicle! Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN today for expert remote support. Our experienced technicians can guide you through the VCDS diagnostic process, help you interpret the data, and provide solutions for complex fuel system problems.
Reach out to us now via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for immediate assistance!
 Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VNLet CAR-CODING.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in car coding and diagnostics.
Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VNLet CAR-CODING.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in car coding and diagnostics.