Modern automotive diagnostics can be complex, but with the right tools, such as VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System), identifying issues like a faulty MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor becomes manageable. At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we offer remote car coding assistance to help technicians navigate these complexities, ensuring accurate diagnostics and effective solutions. Our expert support covers ECU programming, hidden feature activation, and permanent fault code clearing, empowering automotive professionals to enhance their service offerings.
Contents
- 1. What is a MAP Sensor and Why is it Important?
- 2. How Can VCDS Help Diagnose MAP Sensor Issues?
- 3. What are the Key VCDS Measuring Blocks for MAP Sensors?
- 4. What Steps Should I Take to Diagnose a MAP Sensor with VCDS?
- 5. What are Common MAP Sensor Fault Codes and What Do They Mean?
- 6. How Do Vacuum Leaks Affect MAP Sensor Readings?
- 7. What Tools Are Needed to Check for Vacuum Leaks?
- 8. How Do I Interpret MAP Sensor Data from VCDS?
- 9. Can I Test a MAP Sensor with a Multimeter?
- 10. What Are the Symptoms of a Bad MAP Sensor?
- 11. Can I Clean a MAP Sensor?
- 12. When Should I Replace a MAP Sensor?
- 13. How Do I Replace a MAP Sensor?
- 14. What is the Difference Between a MAP Sensor and a MAF Sensor?
- 15. How Does Altitude Affect MAP Sensor Readings?
- 16. How Can Remote Car Coding Assistance Help with MAP Sensor Diagnostics?
- 17. What are the Benefits of Using VCDS for Car Diagnostics?
- 18. How Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Ensure Accurate Diagnostics?
- 19. What Types of Vehicles Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Support?
- 20. What Other Services Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Offer?
- 21. How Can I Get Remote Car Coding Assistance from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN?
- 22. What Equipment Do I Need for Remote Car Coding Assistance?
- 23. What Makes CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Different from Other Coding Services?
- 24. Are There Any Risks Involved in Coding a Car’s ECU?
- 25. How Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Minimize Risks During Remote Coding?
- 26. What Should I Do if Something Goes Wrong During Remote Coding?
- 27. How Can I Verify That the Coding Changes Were Successful?
- 28. What are Some Examples of Hidden Features That Can Be Activated?
- 29. How Can Activating Hidden Features Enhance My Car’s Functionality?
- 30. What is the Cost of Remote Car Coding Assistance?
- 31. What Payment Methods Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Accept?
- 32. Can I Get a Refund if I’m Not Satisfied with the Service?
- 33. How Long Does a Remote Coding Session Typically Take?
- 34. What Are the System Requirements for Remote Access Software?
- 35. What Should I Do to Prepare for a Remote Coding Session?
- 36. Will Coding Affect My Car’s Fuel Efficiency?
- 37. Are There Any Legal Restrictions on Coding a Car?
1. What is a MAP Sensor and Why is it Important?
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor plays a critical role in an engine’s operation. The MAP sensor measures the pressure inside the intake manifold. This information is vital for the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the correct air-fuel mixture. The ECU adjusts fuel delivery and ignition timing based on the MAP sensor’s readings.
- Without accurate MAP sensor data, the engine may experience several problems, including:
- Poor fuel economy
- Reduced engine performance
- Increased emissions
- Rough idling or stalling
Understanding the MAP sensor’s function is essential for diagnosing engine-related issues, making it a key component for automotive technicians.
2. How Can VCDS Help Diagnose MAP Sensor Issues?
VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System) is a powerful diagnostic tool for vehicles, particularly those from the Volkswagen Audi Group (VAG). VCDS allows technicians to access and interpret data from the vehicle’s ECU, including MAP sensor readings. By using VCDS, you can monitor the MAP sensor’s performance under various conditions, compare actual readings with expected values, and identify potential problems.
-
VCDS provides several diagnostic functions for MAP sensors:
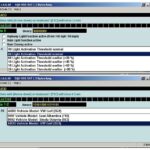
- Reading Measuring Blocks: VCDS allows you to view real-time data from the MAP sensor in measuring blocks. These blocks display the current pressure readings from the sensor.
- Comparing Actual vs. Requested Values: VCDS enables you to compare the actual MAP sensor readings with the values requested by the ECU. Discrepancies between these values can indicate a faulty sensor or vacuum leak.
- Graphing Data: VCDS can graph MAP sensor data, allowing you to visualize the sensor’s performance over time. This is particularly useful for identifying intermittent issues or performance drops under specific conditions.
- Fault Code Scanning: VCDS can scan for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor. These codes can provide clues about the nature of the problem and guide your diagnostic process.
3. What are the Key VCDS Measuring Blocks for MAP Sensors?
When diagnosing MAP sensor issues with VCDS, several measuring blocks provide valuable data. These blocks contain real-time information about the sensor’s performance, allowing you to identify discrepancies and potential problems. Here are some key measuring blocks to monitor:
- Absolute Manifold Pressure (Actual): This block displays the current pressure reading from the MAP sensor in kPa (kilopascals) or mbar (millibars).
- Absolute Manifold Pressure (Specified): This block shows the pressure value that the ECU expects from the MAP sensor under the current conditions. Comparing this value with the actual pressure can help identify issues.
- Engine Speed (RPM): Monitoring engine speed is important because MAP sensor readings should correlate with engine load and RPM.
- Throttle Position: This block indicates the position of the throttle, which also affects manifold pressure.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): Although the MAP sensor and MAF sensor have different functions, they both contribute to determining the air-fuel mixture. Monitoring MAF values can provide additional insights.
4. What Steps Should I Take to Diagnose a MAP Sensor with VCDS?
Diagnosing a MAP sensor with VCDS involves a systematic approach to ensure accurate results. Follow these steps to effectively diagnose MAP sensor issues:
- Connect VCDS to the Vehicle: Connect the VCDS interface to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and start the VCDS software on your computer.
- Select the Engine Control Module: Choose the engine control module (ECU) from the list of available modules.
- Access Measuring Blocks: Navigate to the “Measuring Blocks” function in VCDS.
- Choose Relevant Measuring Blocks: Select the measuring blocks related to the MAP sensor, such as “Absolute Manifold Pressure (Actual)” and “Absolute Manifold Pressure (Specified).”
- Monitor Data at Idle: Start the engine and monitor the MAP sensor readings at idle. Compare the actual and specified values to see if they match.
- Test Under Load: Perform a test drive or run the engine under varying load conditions. Observe how the MAP sensor readings change.
- Graph the Data: Use VCDS to graph the MAP sensor data during the test. This helps visualize any inconsistencies or drops in performance.
- Check for Fault Codes: Scan for any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor. These codes can provide additional information about the issue.
- Interpret the Results: Analyze the data and fault codes to determine if the MAP sensor is faulty or if there is another underlying problem, such as a vacuum leak.
By following these steps, you can effectively use VCDS to diagnose MAP sensor issues and identify the root cause of engine-related problems.
5. What are Common MAP Sensor Fault Codes and What Do They Mean?
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem. Here are some common MAP sensor fault codes and their meanings:
- P0105 – Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Malfunction: This code indicates a general problem with the MAP sensor circuit, such as a wiring issue or a faulty sensor.
- P0106 – Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Range/Performance Problem: This code suggests that the MAP sensor readings are out of the expected range, possibly due to a sensor failure or a vacuum leak.
- P0107 – Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Low Input: This code indicates that the MAP sensor is sending a low voltage signal, which may be caused by a short circuit or a faulty sensor.
- P0108 – Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit High Input: This code suggests that the MAP sensor is sending a high voltage signal, possibly due to an open circuit or a faulty sensor.
- P1114 – Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Short to Ground: This code indicates that the MAP sensor signal wire is shorted to ground, leading to incorrect readings.
When you encounter these fault codes, it is essential to perform further diagnostics to pinpoint the exact cause of the problem. This may involve checking the sensor’s wiring, vacuum lines, and the sensor itself.
6. How Do Vacuum Leaks Affect MAP Sensor Readings?
Vacuum leaks can significantly impact MAP sensor readings and engine performance. The MAP sensor measures the pressure in the intake manifold, and any leaks in the vacuum system can cause inaccurate readings. Here’s how vacuum leaks affect MAP sensor readings:
- Lean Air-Fuel Mixture: Vacuum leaks introduce unmetered air into the intake manifold, leading to a lean air-fuel mixture. This means that there is more air than fuel in the mixture, which can cause the engine to run poorly.
- Incorrect MAP Sensor Readings: A vacuum leak causes the MAP sensor to read a higher pressure than actual. The ECU interprets this as a lower engine load and reduces fuel delivery, further exacerbating the lean condition.
- Rough Idle: Vacuum leaks often result in a rough or unstable idle. The engine may struggle to maintain a consistent RPM, leading to stalling or erratic behavior.
- Reduced Engine Performance: The lean air-fuel mixture and incorrect MAP sensor readings can reduce overall engine performance. The engine may feel sluggish, and acceleration may be poor.
Identifying and repairing vacuum leaks is crucial for maintaining accurate MAP sensor readings and optimal engine performance. Common sources of vacuum leaks include cracked or damaged vacuum lines, faulty intake manifold gaskets, and leaking PCV valves.
7. What Tools Are Needed to Check for Vacuum Leaks?
Checking for vacuum leaks requires some basic tools and equipment. Here are some essential tools for detecting vacuum leaks:
- Smoke Machine: A smoke machine is one of the most effective tools for detecting vacuum leaks. It introduces smoke into the intake manifold, and any leaks will be visible as smoke escaping from the system.
- Vacuum Gauge: A vacuum gauge can be used to measure the vacuum pressure in the intake manifold. Abnormal readings can indicate a vacuum leak.
- Carburetor Cleaner or Propane Torch: These can be used to locate vacuum leaks by spraying them around vacuum lines and intake manifold gaskets. If the engine RPM changes, it indicates a leak in that area.
- Handheld Vacuum Pump: A handheld vacuum pump can be used to test individual vacuum components, such as the VNT actuator and one-way valves.
- Visual Inspection: A thorough visual inspection of all vacuum lines and components can often reveal obvious cracks or damage.
Using these tools will help you systematically identify and repair vacuum leaks, ensuring accurate MAP sensor readings and optimal engine performance.
Alt: Vacuum hose inspection showing cracked and damaged rubber hose, indicative of a vacuum leak requiring immediate repair.
8. How Do I Interpret MAP Sensor Data from VCDS?
Interpreting MAP sensor data from VCDS requires understanding the expected values and how they correlate with engine conditions. Here are some guidelines for interpreting MAP sensor data:
- Idle Readings: At idle, the MAP sensor should read approximately 25-45 kPa (kilopascals) or 250-450 mbar (millibars), depending on altitude and engine type. Higher readings may indicate a vacuum leak or a faulty sensor.
- Wide Open Throttle (WOT): At wide open throttle, the MAP sensor should read close to atmospheric pressure, typically around 90-105 kPa (900-1050 mbar). Lower readings may indicate a restriction in the intake system or a faulty sensor.
- Correlation with Engine Speed: MAP sensor readings should correlate with engine speed (RPM). As engine speed increases, the MAP sensor reading should also increase.
- Comparison with Specified Values: Compare the actual MAP sensor readings with the specified values from the ECU. Significant discrepancies may indicate a problem with the sensor or the vacuum system.
- Smooth Transitions: The MAP sensor readings should transition smoothly as the engine load changes. Sudden spikes or drops in the readings may indicate a faulty sensor.
By understanding these guidelines, you can effectively interpret MAP sensor data from VCDS and identify potential problems with the sensor or the engine’s vacuum system.
9. Can I Test a MAP Sensor with a Multimeter?
Yes, you can test a MAP sensor with a multimeter to check its voltage and resistance. This can help determine if the sensor is functioning correctly. Here’s how to test a MAP sensor with a multimeter:
- Identify the Sensor Terminals: Locate the MAP sensor and identify the power, ground, and signal terminals. Refer to the vehicle’s wiring diagram for the correct terminal identification.
- Check Power Supply: With the ignition on, use the multimeter to check the voltage between the power and ground terminals. You should see approximately 5 volts.
- Check Ground Connection: Use the multimeter to check the continuity between the ground terminal and the vehicle’s chassis. You should have a good ground connection with minimal resistance.
- Check Signal Voltage: With the engine running, use the multimeter to check the voltage on the signal terminal. The voltage should vary as the engine load changes. At idle, the voltage is typically around 1-1.5 volts, and it should increase as the throttle is opened.
- Compare with Specifications: Compare the measured voltage values with the manufacturer’s specifications. Significant deviations may indicate a faulty sensor.
Testing the MAP sensor with a multimeter can help you identify electrical issues, such as a lack of power supply or a faulty signal. However, it may not detect all types of sensor problems, such as those related to internal calibration or response time.
10. What Are the Symptoms of a Bad MAP Sensor?
A faulty MAP sensor can cause a variety of engine-related problems. Recognizing the symptoms of a bad MAP sensor can help you diagnose the issue quickly. Here are some common symptoms:
- Poor Fuel Economy: An inaccurate MAP sensor can cause the engine to run rich or lean, leading to decreased fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Engine Performance: The engine may feel sluggish, and acceleration may be poor due to incorrect air-fuel mixture.
- Rough Idle: A bad MAP sensor can cause the engine to idle roughly or stall, especially at low speeds.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light may illuminate, and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor may be stored in the ECU.
- Black Smoke from Exhaust: A rich air-fuel mixture caused by a faulty MAP sensor can result in black smoke coming from the exhaust.
- Failed Emissions Test: An improperly functioning MAP sensor can cause the vehicle to fail an emissions test due to increased levels of pollutants.
If you notice these symptoms, it is essential to diagnose the MAP sensor using VCDS or a multimeter to determine if it is the cause of the problem.
11. Can I Clean a MAP Sensor?
Yes, you can attempt to clean a MAP sensor, but it should be done with caution. Cleaning a MAP sensor can sometimes restore its functionality, but it is not always a permanent solution. Here’s how to clean a MAP sensor:
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the MAP sensor from the vehicle’s wiring harness.
- Inspect the Sensor: Visually inspect the sensor for any signs of dirt, oil, or other contaminants.
- Use a MAP Sensor Cleaner: Use a specialized MAP sensor cleaner or electronic component cleaner. These cleaners are designed to dissolve contaminants without damaging the sensor.
- Spray the Sensor: Spray the cleaner onto the sensor element, being careful not to touch it directly.
- Allow to Dry: Allow the sensor to air dry completely before reinstalling it.
- Reinstall the Sensor: Reinstall the MAP sensor and reconnect the wiring harness.
- Test the Sensor: Use VCDS or a multimeter to test the sensor and ensure that it is functioning correctly.
Cleaning a MAP sensor can sometimes resolve issues caused by contamination, but if the sensor is internally damaged, it will need to be replaced.
12. When Should I Replace a MAP Sensor?
Deciding when to replace a MAP sensor depends on the diagnostic results and the sensor’s condition. Here are some situations where replacing a MAP sensor is recommended:
- Faulty Readings: If the MAP sensor is consistently providing inaccurate readings, even after cleaning and testing, it should be replaced.
- Internal Damage: If the sensor is physically damaged or shows signs of internal failure, it should be replaced.
- Non-Responsive: If the sensor is not responding to changes in engine load or is not providing any signal, it should be replaced.
- Recurring Fault Codes: If the MAP sensor is triggering recurring fault codes, even after troubleshooting the wiring and vacuum system, it should be replaced.
- Old Age: If the MAP sensor is old and has been in service for many years, it may be prudent to replace it as a preventative measure.
Replacing a faulty MAP sensor can restore proper engine performance, improve fuel economy, and prevent potential damage to other engine components.
13. How Do I Replace a MAP Sensor?
Replacing a MAP sensor is a straightforward process that can be done with basic tools. Here’s how to replace a MAP sensor:
- Gather Tools and Parts: Collect the necessary tools, including a socket set, wrench, and the new MAP sensor.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shorts.
- Locate the MAP Sensor: Locate the MAP sensor on the intake manifold or throttle body.
- Disconnect the Wiring Harness: Disconnect the wiring harness from the MAP sensor.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use a socket or wrench to remove the old MAP sensor from the intake manifold.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new MAP sensor, making sure to tighten it to the proper torque specification.
- Reconnect the Wiring Harness: Reconnect the wiring harness to the MAP sensor.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Test the Sensor: Start the engine and use VCDS or a multimeter to test the new MAP sensor and ensure that it is functioning correctly.
Replacing the MAP sensor can resolve many engine-related issues and restore optimal performance.
14. What is the Difference Between a MAP Sensor and a MAF Sensor?
MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensors and MAF (Mass Air Flow) sensors both measure engine air intake, but they do so in different ways. Here’s a comparison of the two:
- MAP Sensor:
- Function: Measures the pressure in the intake manifold.
- Location: Typically located on the intake manifold or throttle body.
- Output: Provides a pressure reading to the ECU.
- Usage: Commonly used in older vehicles and vehicles with turbochargers.
- MAF Sensor:
- Function: Measures the mass of air flowing into the engine.
- Location: Typically located in the intake air stream, near the air filter box.
- Output: Provides a mass flow reading to the ECU.
- Usage: Commonly used in newer vehicles.
While both sensors provide information about air intake, they do so using different principles. Some vehicles may use both MAP and MAF sensors to provide comprehensive data to the ECU.
15. How Does Altitude Affect MAP Sensor Readings?
Altitude can affect MAP sensor readings because atmospheric pressure decreases as altitude increases. Here’s how altitude affects MAP sensor readings:
- Lower Atmospheric Pressure: At higher altitudes, the atmospheric pressure is lower, which means the MAP sensor will read lower pressure values.
- Impact on Air-Fuel Mixture: The ECU compensates for the lower atmospheric pressure by adjusting the air-fuel mixture.
- Potential for Lean Conditions: If the MAP sensor is not functioning correctly, the ECU may not be able to compensate for the altitude, leading to lean conditions.
When diagnosing MAP sensor issues, it is essential to consider the altitude at which the vehicle is operating. Comparing MAP sensor readings at different altitudes can help identify potential problems.
16. How Can Remote Car Coding Assistance Help with MAP Sensor Diagnostics?
Remote car coding assistance from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can provide valuable support for MAP sensor diagnostics. Here’s how:
- Expert Guidance: Our experienced technicians can provide expert guidance on using VCDS to diagnose MAP sensor issues.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: We can analyze real-time MAP sensor data and help you interpret the results.
- Fault Code Interpretation: We can help you understand the meaning of MAP sensor fault codes and guide you in troubleshooting the problem.
- Remote Support: We can provide remote support to help you perform tests, identify vacuum leaks, and verify sensor functionality.
- Coding and Programming: If the MAP sensor replacement requires coding or programming, we can provide remote assistance to ensure that the new sensor is properly configured.
Our remote car coding assistance can save you time and money by providing expert support and ensuring accurate diagnostics. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for more information. Our office is located at 100 Tech Innovation Dr, Suite 500, San Jose, CA 95110, United States.
17. What are the Benefits of Using VCDS for Car Diagnostics?
VCDS offers several benefits for car diagnostics, especially for Volkswagen Audi Group (VAG) vehicles. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: VCDS provides comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, allowing you to access and interpret data from various vehicle systems.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: VCDS allows you to monitor real-time data from sensors and components, helping you identify issues as they occur.
- Fault Code Scanning: VCDS can scan for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and provide detailed information about the nature of the problem.
- Coding and Programming: VCDS allows you to perform coding and programming functions, such as activating hidden features or adapting new components.
- User-Friendly Interface: VCDS has a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to navigate and use, even for novice technicians.
- Cost-Effective: VCDS is a cost-effective diagnostic tool compared to expensive factory scan tools.
Using VCDS can help you diagnose and repair car problems quickly and efficiently, saving you time and money.
18. How Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Ensure Accurate Diagnostics?
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we prioritize accuracy and reliability in our diagnostic services. Here’s how we ensure accurate diagnostics:
- Experienced Technicians: Our team consists of experienced technicians with extensive knowledge of automotive systems and diagnostic tools.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: We use advanced diagnostic tools, such as VCDS, to access and interpret data from vehicle systems.
- Systematic Approach: We follow a systematic approach to diagnostics, ensuring that all possible causes are investigated.
- Data Analysis: We carefully analyze data from sensors and components to identify discrepancies and potential problems.
- Verification: We verify our diagnostic results by performing tests and inspections to confirm the accuracy of our findings.
- Continuous Training: We provide continuous training to our technicians to keep them up-to-date with the latest diagnostic techniques and technologies.
Our commitment to accuracy and reliability ensures that you receive the best possible diagnostic services.
19. What Types of Vehicles Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Support?
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN supports a wide range of vehicles, including those from the Volkswagen Audi Group (VAG) and other popular brands. Here are some of the vehicle types we support:
- Volkswagen: Golf, Jetta, Passat, Tiguan, Touareg
- Audi: A3, A4, A6, Q5, Q7
- BMW: 3 Series, 5 Series, X3, X5
- Mercedes-Benz: C-Class, E-Class, S-Class, GLC, GLE
- Skoda: Octavia, Superb, Kodiaq
- SEAT: Leon, Ibiza, Ateca
- Porsche: Cayenne, Macan, Panamera
Our expertise extends to a variety of makes and models, ensuring that we can provide comprehensive diagnostic and coding services for your vehicle.
20. What Other Services Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Offer?
In addition to MAP sensor diagnostics, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers a wide range of automotive services, including:
- ECU Programming: We provide ECU programming services to update or modify the software in your vehicle’s engine control unit.
- Car Coding: We offer car coding services to activate hidden features, customize vehicle settings, and improve performance.
- Remote Car Coding Assistance: We provide remote car coding assistance to help you perform coding and programming tasks from anywhere.
- Fault Code Clearing: We can clear fault codes and reset warning lights in your vehicle’s ECU.
- Hidden Feature Activation: We can activate hidden features in your vehicle, such as cornering lights, emergency braking display, and more.
- Performance Tuning: We offer performance tuning services to improve your vehicle’s horsepower, torque, and fuel economy.
Our comprehensive range of services ensures that we can meet all of your automotive needs.
21. How Can I Get Remote Car Coding Assistance from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN?
Getting remote car coding assistance from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN is easy. Follow these steps:
- Contact Us: Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN.
- Describe Your Issue: Describe the issue you are experiencing and the type of assistance you need.
- Provide Vehicle Information: Provide us with the make, model, and year of your vehicle, as well as any relevant diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Schedule a Session: Schedule a remote assistance session with one of our experienced technicians.
- Connect to Your Vehicle: Connect your computer to your vehicle using a compatible diagnostic tool.
- Receive Remote Assistance: Our technician will connect to your computer remotely and provide step-by-step guidance to help you diagnose and resolve the issue.
Our remote car coding assistance is fast, convenient, and affordable. Contact us today to get started.
22. What Equipment Do I Need for Remote Car Coding Assistance?
To receive remote car coding assistance from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, you will need the following equipment:
- Laptop: A laptop with a stable internet connection.
- Diagnostic Tool: A compatible diagnostic tool, such as VCDS or OBDeleven.
- OBD-II Cable: An OBD-II cable to connect the diagnostic tool to your vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Remote Access Software: Remote access software, such as TeamViewer or AnyDesk.
Ensure that you have all of the necessary equipment before your remote assistance session to ensure a smooth and efficient experience.
23. What Makes CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Different from Other Coding Services?
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN stands out from other coding services due to our commitment to excellence, expertise, and customer satisfaction. Here’s what makes us different:
- Experienced Technicians: Our team consists of experienced technicians with extensive knowledge of automotive systems and coding techniques.
- Comprehensive Services: We offer a comprehensive range of services, including ECU programming, car coding, fault code clearing, and more.
- Remote Assistance: We provide remote assistance to help you perform coding and programming tasks from anywhere.
- Affordable Pricing: We offer competitive pricing for our services, making them accessible to a wide range of customers.
- Customer Support: We provide excellent customer support, ensuring that you receive the assistance you need when you need it.
- Commitment to Quality: We are committed to providing high-quality services that meet or exceed your expectations.
Choose CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for reliable, expert, and affordable car coding services.
24. Are There Any Risks Involved in Coding a Car’s ECU?
Yes, there are potential risks involved in coding a car’s ECU. It’s crucial to understand these risks before proceeding:
- Data Corruption: Incorrect coding can lead to data corruption in the ECU, potentially causing malfunctions.
- System Instability: Improper coding can destabilize the car’s systems, leading to unpredictable behavior.
- Warranty Issues: Modifying the ECU can void the car’s warranty, leaving you responsible for repairs.
- Software Conflicts: Coding errors can cause conflicts with other software systems in the car.
- Immobilization: In severe cases, incorrect coding can immobilize the car, rendering it unusable.
To mitigate these risks, it’s best to seek professional assistance from experienced technicians like those at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN.
25. How Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Minimize Risks During Remote Coding?
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN takes several precautions to minimize risks during remote coding sessions:
- Experienced Technicians: We employ highly skilled and experienced technicians who understand the intricacies of ECU coding.
- Verified Software: We use verified and tested software to ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Backup Procedures: We create backups of the original ECU data before making any changes, allowing us to revert to the original state if necessary.
- Step-by-Step Guidance: We provide clear, step-by-step guidance throughout the coding process to minimize the risk of errors.
- Real-Time Monitoring: We monitor the coding process in real-time to detect and address any issues that may arise.
- Error Checking: We perform thorough error checking after coding to ensure that all systems are functioning correctly.
Our commitment to safety and quality minimizes the risks associated with ECU coding.
26. What Should I Do if Something Goes Wrong During Remote Coding?
If something goes wrong during remote coding, follow these steps:
- Stay Calm: It’s important to remain calm and not panic.
- Contact Us Immediately: Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN immediately via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
- Do Not Disconnect: Do not disconnect the diagnostic tool or turn off the car unless instructed to do so.
- Provide Details: Provide our technician with as much detail as possible about what happened and any error messages you received.
- Follow Instructions: Follow our technician’s instructions carefully. They will guide you through the necessary steps to resolve the issue.
- Be Patient: Resolving coding issues can take time, so be patient and allow our technician to work through the problem.
Our experienced technicians are equipped to handle coding issues and will work diligently to restore your car’s systems to their proper state.
27. How Can I Verify That the Coding Changes Were Successful?
After completing the coding changes, verify their success:
- Test the Features: Test the newly coded features to ensure they are functioning as expected.
- Check for Error Codes: Use a diagnostic tool like VCDS to scan for any new error codes that may have been introduced.
- Monitor Performance: Monitor the car’s performance over the next few days to ensure that there are no adverse effects.
- Review Documentation: Review the coding documentation to ensure that all steps were followed correctly.
- Consult with Experts: If you have any concerns, consult with the experts at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN to verify the coding changes.
Verifying the coding changes ensures that the car is functioning correctly and that the new features are working as intended.
28. What are Some Examples of Hidden Features That Can Be Activated?
Many cars have hidden features that can be activated through coding. Some examples include:
- Cornering Lights: Activating cornering lights to improve visibility when turning.
- Emergency Braking Display: Enabling the emergency braking display to alert drivers behind you during hard braking.
- Gauge Staging: Activating gauge staging, where the instrument cluster needles sweep to their maximum and return upon startup.
- Acoustic Confirmation: Enabling acoustic confirmation when locking and unlocking the car.
- Video in Motion: Allowing video playback on the infotainment system while the car is moving.
- Comfort Turn Signal: Adjusting the number of flashes for the comfort turn signal.
These are just a few examples of the many hidden features that can be activated through coding.
29. How Can Activating Hidden Features Enhance My Car’s Functionality?
Activating hidden features can significantly enhance your car’s functionality:
- Improved Safety: Features like cornering lights and emergency braking display can improve safety by increasing visibility and alerting other drivers.
- Increased Convenience: Features like acoustic confirmation and comfort turn signal can increase convenience and ease of use.
- Personalized Experience: Activating hidden features allows you to personalize your car to your preferences and needs.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Features like gauge staging can enhance the car’s aesthetics and create a more engaging driving experience.
- Added Value: Activating hidden features can add value to your car and make it more enjoyable to own.
Activating hidden features is a great way to get more out of your car and enhance its functionality.
Alt: Car coding setup showcasing a technician using a laptop and diagnostic tool connected to a car, emphasizing the technology-driven approach to modern automotive maintenance.
30. What is the Cost of Remote Car Coding Assistance?
The cost of remote car coding assistance varies depending on the complexity of the task and the time required. At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we offer competitive pricing for our services. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for a customized quote. Our pricing is transparent and affordable, ensuring you get the best value for your money. We also offer package deals and discounts for repeat customers.
31. What Payment Methods Does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN Accept?
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN accepts a variety of payment methods for your convenience:
- Credit Cards: We accept major credit cards, including Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover.
- Debit Cards: We accept debit cards with a Visa or Mastercard logo.
- PayPal: You can pay securely through PayPal.
- Bank Transfers: We accept bank transfers for larger transactions.
We ensure secure payment processing to protect your financial information.
32. Can I Get a Refund if I’m Not Satisfied with the Service?
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we strive for customer satisfaction. If you are not satisfied with our service, please contact us immediately. We will do our best to resolve the issue. We offer a refund policy on a case-by-case basis, depending on the circumstances. Our goal is to ensure that you are happy with the service you receive. We value your business and are committed to providing excellent customer service.
33. How Long Does a Remote Coding Session Typically Take?
The duration of a remote coding session varies depending on the complexity of the task. Simple coding tasks may take as little as 30 minutes, while more complex tasks can take several hours. At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we provide an estimated time frame before the session begins. We work efficiently to minimize downtime and ensure that the coding is completed accurately. Our technicians are skilled at managing their time effectively, so you can be confident that the session will be completed in a timely manner.
34. What Are the System Requirements for Remote Access Software?
To use remote access software for car coding, ensure your system meets these requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 7 or later, macOS 10.10 or later.
- Internet Connection: A stable, high-speed internet connection (at least 5 Mbps).
- RAM: At least 4 GB of RAM.
- Processor: Intel Core i3 or equivalent.
- Software: Download and install TeamViewer or AnyDesk.
- Firewall: Configure your firewall to allow remote access software.
- Administrator Privileges: You need administrator privileges to install and run the software.
Meeting these requirements will ensure a smooth remote access session.
35. What Should I Do to Prepare for a Remote Coding Session?
To prepare for a remote coding session:
- Charge Your Laptop: Ensure your laptop is fully charged or plugged in.
- Stable Internet: Verify you have a stable internet connection.
- Install Software: Install TeamViewer or AnyDesk.
- Gather Information: Have your vehicle’s make, model, and VIN ready.
- Diagnostic Tool: Connect your diagnostic tool to your car.
- Clear Workspace: Ensure a quiet workspace free from distractions.
- Disable Antivirus: Temporarily disable antivirus software if it interferes.
- Backup Data: Backup important data on your laptop.
- Follow Instructions: Follow all instructions from the technician.
- Be Patient: Coding can take time, so be patient.
Preparing ensures a successful and efficient coding session.
36. Will Coding Affect My Car’s Fuel Efficiency?
Coding can affect a car’s fuel efficiency depending on the changes made. Some coding adjustments can improve fuel efficiency, while others may decrease it. For example, optimizing engine parameters can lead to better fuel economy. However, activating performance-enhancing features might increase fuel consumption. Consult with the experts at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN to understand how specific coding changes will impact your car’s fuel efficiency. They can provide guidance on achieving the desired balance between performance and economy.
37. Are There Any Legal Restrictions on Coding a Car?
Legal restrictions on coding a car vary by region