Navigating the complexities of modern car coding requires specialized tools, and the Inpa Vcds Interface emerges as a popular option, that CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, offering expert remote support, to ensure safety and efficiency in your coding tasks. With our remote automotive coding support, we empower technicians to activate hidden features, clear fault codes, and program ECUs with confidence.
Contents
- 1. What is an INPA VCDS Interface and How Does It Work?
- INPA: BMW’s Diagnostic Powerhouse
- VCDS: Unlocking VAG Vehicle Potential
- Key Differences and Compatibility Considerations
- 2. What are the Benefits of Using an INPA VCDS Interface for Car Coding?
- 3. Is it Possible to Use an Old VCDS Cable for Newer BMWs with INPA Software?
- Understanding Protocol Differences
- Potential Risks of Mismatched Interfaces
- The Importance of Proper Interface Selection
- 4. Can Shorting Pin 7 and 8 on a VCDS Cable Make it Compatible with BMW INPA?
- Why Pin Shorting is an Overly Simplistic Approach
- The Importance of Protocol-Specific Interfaces
- CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Safe and Effective Car Coding
- 5. What Modifications are Needed to Make an OBD-II Interface Fully Compatible with BMW Diagnostics?
- Detailed Explanation of Necessary Modifications
- The Importance of Accurate Implementation
- CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Trusted Partner for BMW Diagnostics
- 6. What Does a True KL Interface Look Like for Standard OBD-II Serial Diagnosis Software?
- Essential Components and Functionality
- Distinguishing a True KL Interface from Counterfeit Versions
- CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Reliable Diagnostic Solutions
- 7. What Modifications Does a Standard OBD-II Serial KL Interface Need to Be BMW Diagnosis Compatible?
- Step-by-Step Guide to Modifying Your OBD-II Interface
- Safety Precautions and Best Practices
- CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Safe and Effective Car Coding
- 8. Are INPA Cables from China Reliable Copies of the Interface Schematic?
- Factors Affecting the Reliability of Chinese INPA Cables
- Tips for Verifying the Reliability of Chinese INPA Cables
- CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Reliable Car Coding Solutions
- 9. How Can I Ensure My INPA VCDS Interface is Working Correctly?
- Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Your INPA VCDS Interface
- Troubleshooting Common Interface Issues
- CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Reliable Car Coding Solutions
- 10. What are the Risks of Using a Faulty or Incompatible INPA VCDS Interface?
- Specific Risks Associated with Faulty Interfaces
- Real-World Examples of Interface-Related Damage
- CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Safe and Reliable Car Coding
- FAQ: INPA VCDS Interface
- 1. Is it safe to perform car coding with an INPA VCDS interface?
- 2. What is the process for remote coding support with CAR-CODING.EDU.VN?
- 3. How much does remote coding support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN cost?
- 4. What types of vehicles and features does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN support for remote coding?
- 5. What equipment is required on my end to receive remote coding support?
- 6. What happens if something goes wrong during the coding process?
- 7. Can I activate hidden features on my car using remote coding support?
- 8. Is remote coding support available for all car models and years?
- 9. How long does a typical remote coding session take?
- 10. What are the benefits of choosing CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for remote coding support?
1. What is an INPA VCDS Interface and How Does It Work?
An INPA (Interface for Programmierung, Codierung und Applikation) VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System) interface serves as a crucial link between your computer and your vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs), facilitating diagnostics, coding, and programming, however the INPA is used for BMW cars and the VCDS is used for VW, Audi, Seat and Skoda cars. This interface enables technicians to access and modify various parameters within the car’s systems. INPA primarily supports BMW vehicles, while VCDS caters to Volkswagen, Audi, Seat, and Skoda (VAG) models. By connecting to the car’s OBD-II port, the interface allows software like INPA or VCDS to communicate with the ECUs, enabling tasks such as reading fault codes, clearing errors, and performing coding operations. Understanding the specific protocols and capabilities of each interface is essential for effective car coding and diagnostics.
INPA: BMW’s Diagnostic Powerhouse
INPA, short for Interface for Programming Applications, represents BMW’s proprietary diagnostic software. Designed primarily for internal use within BMW dealerships and service centers, INPA provides comprehensive access to the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs). This access allows technicians to perform a wide array of functions, including:
- Reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Accessing real-time data from various sensors and modules.
- Performing advanced coding and programming operations.
- Enabling or disabling specific vehicle features.
INPA’s capabilities extend to a wide range of BMW models, from older E-series to newer F- and G-series vehicles. Its robust functionality and deep-level access make it an indispensable tool for BMW technicians and enthusiasts alike.
VCDS: Unlocking VAG Vehicle Potential
VCDS, or VAG-COM Diagnostic System, serves as the go-to diagnostic and coding software for vehicles within the Volkswagen Audi Group (VAG). This includes Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT models. Developed by Ross-Tech, VCDS offers similar functionality to INPA but is tailored specifically for VAG vehicles. Key features of VCDS include:
- Comprehensive fault code reading and clearing.
- Access to live data and measuring blocks.
- Adaptation and coding of control modules.
- Enabling hidden features and customizations.
VCDS’s user-friendly interface and extensive support for VAG vehicles have made it a popular choice among independent repair shops, enthusiasts, and tuners. Its ability to unlock hidden features and customize vehicle behavior has further solidified its position in the VAG community.
Key Differences and Compatibility Considerations
While both INPA and VCDS serve similar purposes, they differ significantly in their target vehicles and software architecture. INPA is exclusively designed for BMW vehicles, while VCDS caters to VAG models. Attempting to use INPA on a VAG vehicle or vice versa will result in communication errors and potential damage to the vehicle’s electronics.
Furthermore, the interfaces and protocols used by INPA and VCDS differ. INPA typically requires a specialized interface cable that supports BMW’s diagnostic protocols, while VCDS utilizes a proprietary interface developed by Ross-Tech. These interfaces are not interchangeable, and using the wrong interface can lead to communication problems or even damage to the vehicle’s ECUs.
2. What are the Benefits of Using an INPA VCDS Interface for Car Coding?
Employing an INPA VCDS interface for car coding unlocks a multitude of benefits, including the ability to customize vehicle behavior, activate hidden features, and perform advanced diagnostics. Technicians can tailor the car’s settings to individual preferences, such as adjusting lighting parameters, enabling comfort features, and optimizing performance settings. Moreover, these interfaces facilitate in-depth diagnostics, allowing for accurate identification and resolution of complex issues. By leveraging the capabilities of INPA or VCDS, technicians can enhance their diagnostic skills and provide personalized solutions for their customers.
- Personalization: Tailor your vehicle’s functions to your specific preferences.
- Diagnostics: Identify and resolve complex issues accurately.
- Hidden Features: Unlock capabilities that were not initially activated by the manufacturer.
- Performance Tuning: Optimize your car’s performance parameters for enhanced driving experience.
- Cost Savings: Perform diagnostics and coding yourself, reducing the need for expensive dealership visits.
3. Is it Possible to Use an Old VCDS Cable for Newer BMWs with INPA Software?
Using an old VCDS cable for newer BMWs with INPA software is generally not recommended due to compatibility issues, as the INPA is used for BMW cars and the VCDS is used for VW, Audi, Seat and Skoda cars. VCDS cables are designed specifically for VAG vehicles and communicate using different protocols than those used by BMWs. INPA software requires a compatible interface that supports BMW’s diagnostic protocols. Attempting to use a VCDS cable with INPA on a BMW may result in communication errors, damage to the vehicle’s ECUs, or failure to establish a connection. It’s crucial to use the appropriate interface and software combination to ensure safe and effective car coding. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides expert guidance on selecting the right tools for your specific vehicle and coding needs, ensuring compatibility and preventing potential issues.
Understanding Protocol Differences
The core reason why a VCDS cable won’t work with INPA lies in the fundamental differences in communication protocols. BMW vehicles rely on protocols like CAN bus, K-line, and MOST bus for communication between ECUs. INPA is designed to communicate using these protocols, sending and receiving data in a format that BMW’s ECUs understand.
VAG vehicles, on the other hand, primarily use the CAN bus protocol, but the specific implementation and data format differ from BMW’s. VCDS is engineered to communicate using VAG-specific protocols, which are incompatible with BMW’s systems.
Potential Risks of Mismatched Interfaces
Attempting to force a VCDS cable to work with INPA can lead to a range of problems, from simple communication errors to severe damage to the vehicle’s electronic systems. Some potential risks include:
- ECU Damage: Sending incorrect signals or data to an ECU can corrupt its firmware, rendering it inoperable.
- Communication Errors: Incompatible protocols can prevent the software from communicating with the vehicle’s ECUs, resulting in inaccurate diagnostics or failed coding attempts.
- Data Corruption: Incorrect data transmission can corrupt stored data within the ECUs, leading to unpredictable vehicle behavior.
- Interface Damage: Attempting to use an incompatible interface can damage the interface itself, rendering it useless.
The Importance of Proper Interface Selection
To ensure safe and effective car coding and diagnostics, it’s crucial to use the correct interface and software combination. Always verify that the interface is specifically designed for the target vehicle and that the software is compatible with the interface.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers expert guidance on selecting the appropriate tools for your specific vehicle and coding needs. Our team can help you identify the right interface and software combination, ensuring compatibility and preventing potential issues.
4. Can Shorting Pin 7 and 8 on a VCDS Cable Make it Compatible with BMW INPA?
Shorting Pin 7 and 8 on a VCDS cable will not make it compatible with BMW INPA, the INPA is used for BMW cars and the VCDS is used for VW, Audi, Seat and Skoda cars. While this modification is sometimes suggested for adapting generic OBD-II cables for use with BMWs, it does not address the fundamental differences in communication protocols and interface requirements. INPA requires a specialized interface that supports BMW’s diagnostic protocols, and shorting pins on a VCDS cable will not replicate this functionality. Attempting to use a modified VCDS cable with INPA may still result in communication errors or damage to the vehicle’s ECUs. For reliable and safe BMW coding, it’s best to invest in a dedicated INPA-compatible interface. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can recommend suitable interfaces and provide expert guidance on their proper use.
Why Pin Shorting is an Overly Simplistic Approach
The idea of shorting pins on an OBD-II cable stems from the fact that different vehicle manufacturers use different pins for specific communication protocols. By shorting certain pins, the theory is that you can create a “universal” cable that can communicate with a wider range of vehicles.
However, this approach is overly simplistic and fails to account for the complexities of modern automotive communication systems. Pin shorting does not address the fundamental differences in communication protocols, data formats, and voltage levels used by different manufacturers.
The Importance of Protocol-Specific Interfaces
Modern vehicles rely on sophisticated communication protocols like CAN bus, K-line, and MOST bus for communication between ECUs. Each protocol requires a specific interface that can translate the data into a format that the vehicle’s ECUs understand.
INPA is designed to communicate using BMW-specific protocols, while VCDS uses protocols tailored for VAG vehicles. Shorting pins on a VCDS cable does not magically transform it into a BMW-compatible interface. It simply creates a potentially unstable and unreliable connection that can lead to communication errors or even damage to the vehicle’s ECUs.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Safe and Effective Car Coding
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of using the right tools for the job. That’s why we offer expert guidance on selecting the appropriate interfaces and software for your specific vehicle and coding needs. Our team can recommend suitable INPA-compatible interfaces for BMW vehicles, ensuring compatibility and preventing potential issues.
We also provide comprehensive training and support to help you master the art of car coding safely and effectively. With our guidance, you can unlock the full potential of your vehicle while minimizing the risk of damage or errors.
5. What Modifications are Needed to Make an OBD-II Interface Fully Compatible with BMW Diagnostics?
To make an OBD-II interface fully compatible with BMW diagnostics, specific modifications are required to align with BMW’s communication protocols, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN experts advise. These modifications typically involve adjustments to the interface’s pin configuration and circuitry to ensure proper communication with BMW ECUs. Common modifications include connecting pins 7 and 8, using DTR instead of RTS, and establishing connections between specific pins through resistors for short protection. Additionally, it’s crucial to ensure that the interface supports the necessary protocols, such as K-line and CAN bus, used by BMW vehicles. By implementing these modifications, an OBD-II interface can be adapted to effectively communicate with BMW diagnostic software like INPA.
Detailed Explanation of Necessary Modifications
To achieve full compatibility with BMW diagnostics, an OBD-II interface requires several key modifications:
- Connecting Pins 7 and 8: This modification bridges the K-line, a communication protocol used by many BMW ECUs. By connecting these pins, the interface can effectively transmit and receive data from the vehicle’s control modules.
- Using DTR Instead of RTS: DTR (Data Terminal Ready) and RTS (Request to Send) are control signals used in serial communication. BMW diagnostics often require the use of DTR instead of RTS for proper communication with the vehicle’s ECUs.
- Pin 1 Connection: Connecting pin 1 of the OBD-II interface to DSR (Data Set Ready) via a 1k resistor provides short protection while enabling communication with specific BMW systems.
- RI (Ring Indicator) Connection: Connecting the RS232 RI pin to OBD pin 16 (+ battery feed) via a 1k resistor and a diode (for polarity protection) allows the interface to detect the vehicle’s battery voltage, ensuring stable communication.
These modifications ensure that the OBD-II interface can properly communicate with BMW’s diagnostic software, such as INPA, and access the full range of diagnostic and coding functions.
The Importance of Accurate Implementation
It’s crucial to implement these modifications accurately to avoid potential damage to the vehicle’s ECUs or the interface itself. Incorrect wiring or improper resistor values can lead to communication errors, data corruption, or even permanent damage to the vehicle’s electronic systems.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN recommends seeking guidance from experienced technicians or utilizing pre-modified interfaces to ensure the modifications are performed correctly. Our team of experts can provide detailed instructions and support to help you modify your OBD-II interface safely and effectively.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Trusted Partner for BMW Diagnostics
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing our customers with the tools and knowledge they need to perform BMW diagnostics and coding with confidence. Our comprehensive range of services includes:
- Expert guidance on interface selection and modification
- Detailed tutorials and training materials
- Remote support from experienced BMW technicians
- Access to a wide range of BMW diagnostic software
With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN as your partner, you can unlock the full potential of your BMW and gain the expertise to perform advanced diagnostics and coding tasks safely and effectively.
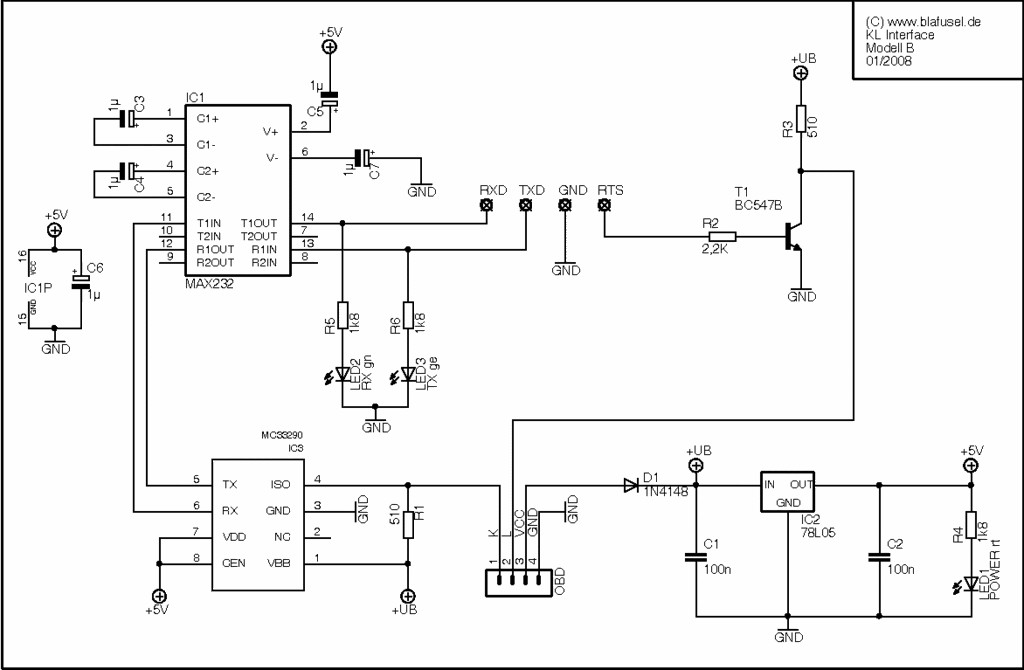 KL Interface Pinouts 1
KL Interface Pinouts 1
6. What Does a True KL Interface Look Like for Standard OBD-II Serial Diagnosis Software?
A true KL interface for standard OBD-II serial diagnosis software features a specific pinout configuration to ensure compatibility with various diagnostic protocols. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN experts highlight that the interface typically includes connections for K-line, L-line, and ground, along with power supply pins. The KL interface enables communication between diagnostic software and the vehicle’s ECUs, allowing for tasks such as reading fault codes, accessing live data, and performing coding operations. Understanding the pinout and functionality of a true KL interface is essential for effective car diagnostics.
Essential Components and Functionality
A true KL interface comprises several essential components that enable seamless communication between diagnostic software and the vehicle’s ECUs:
- K-Line: The K-line serves as the primary communication channel for transmitting data between the interface and the vehicle’s control modules. It operates using a serial communication protocol, allowing for bidirectional data transfer.
- L-Line: The L-line, also known as the diagnostic line, is used for specific diagnostic functions, such as initiating diagnostic sessions and requesting specific data from the ECUs.
- Ground: The ground connection provides a common reference point for the electrical signals, ensuring stable and reliable communication.
- Power Supply: The power supply pins provide the necessary voltage to power the interface’s internal circuitry.
The KL interface’s functionality extends to a wide range of diagnostic tasks, including:
- Reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Accessing live data from various sensors and modules
- Performing actuator tests and component activation
- Coding and programming control modules
- Resetting service reminders and adaptation values
Distinguishing a True KL Interface from Counterfeit Versions
The market is flooded with counterfeit KL interfaces that claim to offer the same functionality as genuine versions. However, these counterfeit interfaces often lack the necessary components and circuitry to ensure reliable communication and may even damage the vehicle’s ECUs.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN advises technicians to be wary of suspiciously cheap interfaces and to purchase from reputable sources that guarantee the authenticity and quality of their products. Key indicators of a true KL interface include:
- Proper pinout configuration and labeling
- High-quality components and soldering
- Compliance with industry standards and certifications
- Positive reviews from other technicians and users
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Reliable Diagnostic Solutions
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing our customers with reliable and high-quality diagnostic solutions. Our range of KL interfaces are sourced from reputable manufacturers and undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
We also offer expert guidance and support to help you select the right interface for your specific needs and to troubleshoot any issues you may encounter. With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN as your partner, you can be confident that you are using a true KL interface that will provide accurate and reliable diagnostic results.
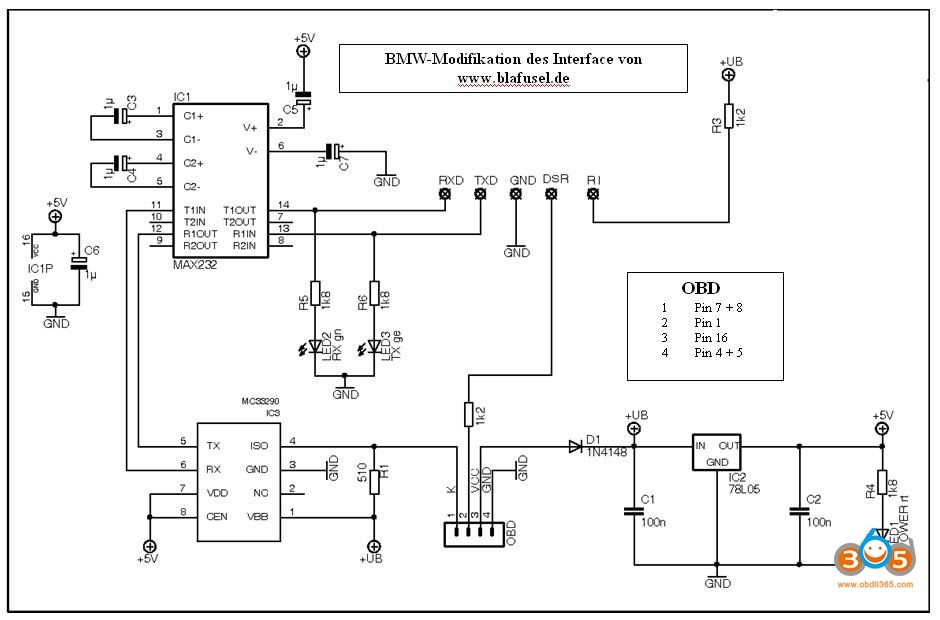 KL Interface Pinouts 2
KL Interface Pinouts 2
7. What Modifications Does a Standard OBD-II Serial KL Interface Need to Be BMW Diagnosis Compatible?
To achieve BMW diagnosis compatibility, a standard OBD-II serial KL interface requires specific modifications to align with BMW’s diagnostic protocols, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN experts explain. These modifications typically involve connecting pins 7 and 8, utilizing DTR instead of RTS, establishing a connection between pin 1 and DSR via a resistor, and connecting the RS232 RI pin with OBD pin 16 through a resistor and diode for short and polarity protection. Implementing these modifications enables the interface to effectively communicate with BMW diagnostic software like INPA, facilitating tasks such as fault code reading, data access, and coding operations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Modifying Your OBD-II Interface
If you’re comfortable with electronics and have the necessary tools, you can modify your standard OBD-II serial KL interface to be BMW diagnosis compatible by following these steps:
- Connect Pins 7 and 8: Use a jumper wire to connect pins 7 and 8 on the OBD-II connector. This bridges the K-line, enabling communication with BMW ECUs.
- Use DTR Instead of RTS: Disconnect the RTS (Request to Send) signal from pin 4 on the sub D RS232 connector and connect the DTR (Data Terminal Ready) signal instead. This ensures proper control signal usage for BMW diagnostics.
- Connect Pin 1 to DSR: Connect pin 1 of the OBD-II connector to DSR (Data Set Ready) on pin 6 of the sub D RS232 connector using a 1k ohm resistor. This provides short protection while enabling communication with specific BMW systems.
- Connect RI to Pin 16: Connect the RS232 RI (Ring Indicator) pin (pin 9 on the sub D RS232 connector) to OBD pin 16 (+ battery feed) using a 1k ohm resistor and a diode for polarity protection. This allows the interface to detect the vehicle’s battery voltage.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
When modifying your OBD-II interface, it’s crucial to follow safety precautions and best practices to avoid potential damage or injury:
- Disconnect Power: Always disconnect the interface from the vehicle and the computer before making any modifications.
- Use Proper Tools: Use appropriate soldering equipment and wiring tools to ensure clean and reliable connections.
- Double-Check Wiring: Carefully double-check all wiring connections before applying power to the interface.
- Seek Expert Guidance: If you’re unsure about any step, seek guidance from experienced technicians or online resources.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Safe and Effective Car Coding
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing our customers with the knowledge and support they need to perform car coding safely and effectively. Our comprehensive range of services includes:
- Expert guidance on interface modification
- Detailed tutorials and training materials
- Remote support from experienced technicians
- Access to a wide range of diagnostic software
With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN as your partner, you can unlock the full potential of your vehicle while minimizing the risk of damage or errors.
8. Are INPA Cables from China Reliable Copies of the Interface Schematic?
INPA cables from China often claim to be copies of the interface schematic, but their reliability can vary significantly, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN cautions. While some cables may closely resemble the original design, others may have quality issues or missing components, leading to unreliable performance. It’s essential to exercise caution when purchasing INPA cables from Chinese manufacturers and to verify their functionality before use. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN recommends sourcing cables from reputable suppliers and conducting thorough testing to ensure compatibility and reliability.
Factors Affecting the Reliability of Chinese INPA Cables
The reliability of INPA cables from China is influenced by several factors:
- Component Quality: The quality of the electronic components used in the cable can vary significantly. Lower-quality components may be more prone to failure, leading to unreliable performance.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process used to assemble the cable can also affect its reliability. Poor soldering, improper wiring, or inadequate quality control can all contribute to issues.
- Design Accuracy: While many Chinese INPA cables claim to be copies of the original schematic, some may have design flaws or missing components that can affect their functionality.
- Software Compatibility: Some Chinese INPA cables may not be fully compatible with all versions of INPA software. This can lead to communication errors or limited functionality.
Tips for Verifying the Reliability of Chinese INPA Cables
Before using a Chinese INPA cable for car coding or diagnostics, it’s essential to verify its reliability by following these tips:
- Purchase from Reputable Suppliers: Choose suppliers with a proven track record of selling high-quality products and providing excellent customer service.
- Check for Positive Reviews: Look for reviews from other users who have purchased and used the cable. Pay attention to comments about reliability, compatibility, and customer support.
- Inspect the Cable Carefully: Examine the cable for any signs of damage, such as loose connections, frayed wires, or cracked components.
- Test the Cable Thoroughly: Connect the cable to your vehicle and use INPA software to perform various diagnostic and coding tasks. Verify that the cable can communicate with all relevant ECUs and that it provides accurate data.
- Compare Results with Known Good Cables: If possible, compare the results obtained with the Chinese INPA cable to those obtained with a known good cable. This can help identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Reliable Car Coding Solutions
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of using reliable and high-quality tools for car coding and diagnostics. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of INPA cables and other diagnostic equipment sourced from reputable manufacturers.
Our cables are rigorously tested to ensure they meet the highest standards of performance and reliability. We also provide expert guidance and support to help you select the right tools for your specific needs and to troubleshoot any issues you may encounter.
With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN as your partner, you can be confident that you are using reliable equipment that will provide accurate and consistent results.
9. How Can I Ensure My INPA VCDS Interface is Working Correctly?
Ensuring your INPA VCDS interface functions correctly requires systematic testing and verification, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN experts advise. Start by confirming proper installation of drivers and software, followed by establishing a stable connection with the vehicle’s OBD-II port. Use diagnostic software to read fault codes and access live data, verifying accurate communication with ECUs. Comparing results with known good data can further validate the interface’s performance. Regular maintenance and updates also contribute to optimal functionality, ensuring reliable car coding and diagnostics.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Your INPA VCDS Interface
Follow these steps to test your INPA VCDS interface and ensure it’s working correctly:
- Verify Driver and Software Installation: Ensure that the correct drivers and software are installed on your computer and that they are compatible with your operating system.
- Establish a Stable Connection: Connect the interface to your vehicle’s OBD-II port and ensure that the connection is stable and secure.
- Check Interface Status: Use the diagnostic software to check the interface status and verify that it is recognized by the software.
- Read Fault Codes: Read fault codes from various ECUs and verify that the interface can retrieve and display the codes accurately.
- Access Live Data: Access live data from various sensors and modules and verify that the interface can display the data in real-time.
- Perform Actuator Tests: Perform actuator tests to activate various components and verify that the interface can control the components as expected.
- Compare Results with Known Good Data: Compare the results obtained with your interface to those obtained with a known good interface or to published specifications. This can help identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies.
- Check for Updates: Regularly check for updates to the interface firmware and software and install them as needed. This can help improve performance and fix any known issues.
Troubleshooting Common Interface Issues
If you encounter any issues while testing your INPA VCDS interface, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Check Connections: Verify that all connections are secure and that there are no loose or damaged wires.
- Restart Computer and Interface: Restart your computer and the interface to clear any temporary glitches or errors.
- Reinstall Drivers and Software: Reinstall the drivers and software to ensure that they are installed correctly and that they are compatible with your operating system.
- Try a Different Vehicle: Try connecting the interface to a different vehicle to rule out any issues with the vehicle’s OBD-II port or ECUs.
- Contact Technical Support: If you’re unable to resolve the issue yourself, contact technical support for assistance.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Reliable Car Coding Solutions
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing our customers with reliable and high-quality car coding solutions. Our comprehensive range of services includes:
- Expert guidance on interface selection and testing
- Detailed tutorials and training materials
- Remote support from experienced technicians
- Access to a wide range of diagnostic software
With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN as your partner, you can be confident that you are using reliable equipment that will provide accurate and consistent results.
10. What are the Risks of Using a Faulty or Incompatible INPA VCDS Interface?
Using a faulty or incompatible INPA VCDS interface poses significant risks to your vehicle’s electronic systems, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN warns. These risks include ECU damage, data corruption, communication errors, and potential safety hazards. A malfunctioning interface may send incorrect signals or data to the ECUs, leading to irreversible damage and costly repairs. Data corruption can result in unpredictable vehicle behavior, while communication errors can prevent proper diagnosis and coding. To mitigate these risks, always ensure that the interface is compatible with your vehicle and software, and conduct thorough testing before use. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides expert guidance on selecting and using the right interface for your specific needs, minimizing the risk of damage or errors.
Specific Risks Associated with Faulty Interfaces
Using a faulty INPA VCDS interface can lead to a variety of specific risks:
- ECU Damage: Incorrect signals or data sent to the ECUs can corrupt their firmware, rendering them inoperable and requiring replacement.
- Data Corruption: Faulty interfaces can corrupt stored data within the ECUs, leading to unpredictable vehicle behavior, such as engine stalling, transmission problems, or airbag malfunction.
- Communication Errors: Incompatible interfaces can prevent the software from communicating with the vehicle’s ECUs, resulting in inaccurate diagnostics or failed coding attempts.
- Safety Hazards: In severe cases, a faulty interface can trigger unintended activation of safety systems, such as airbags or ABS, posing a safety hazard to the driver and passengers.
Real-World Examples of Interface-Related Damage
Here are some real-world examples of damage caused by faulty or incompatible INPA VCDS interfaces:
- A technician used an incompatible interface to attempt to code a BMW ECU, resulting in irreversible damage to the ECU and requiring a costly replacement.
- A DIY enthusiast used a faulty interface to clear fault codes on a Volkswagen, but the interface corrupted the ECU’s data, causing the engine to stall repeatedly.
- A repair shop used a counterfeit interface to perform diagnostics on an Audi, but the interface triggered the unintended activation of the airbags, causing injuries to the technician.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN: Your Partner for Safe and Reliable Car Coding
At CAR-CODING.EDU.VN, we prioritize the safety and reliability of our car coding solutions. That’s why we offer:
- Expert guidance on interface selection and compatibility
- High-quality interfaces sourced from reputable manufacturers
- Thorough testing and verification of all equipment
- Comprehensive training and support to help you avoid potential risks
With CAR-CODING.EDU.VN as your partner, you can be confident that you are using safe and reliable equipment that will protect your vehicle’s electronic systems and ensure accurate results.
Are you facing challenges with car coding and need expert assistance? Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN now via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for immediate remote coding support and guidance. Our office is located at 100 Tech Innovation Dr, Suite 500, San Jose, CA 95110, United States.
FAQ: INPA VCDS Interface
1. Is it safe to perform car coding with an INPA VCDS interface?
Yes, car coding with an INPA VCDS interface can be safe if performed correctly, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN experts assure. However, it requires a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s systems, the coding procedures, and the potential risks involved. Using a reliable interface, following proper procedures, and having expert guidance are essential for safe car coding.
2. What is the process for remote coding support with CAR-CODING.EDU.VN?
The process for remote coding support with CAR-CODING.EDU.VN involves connecting your computer to the vehicle’s OBD-II port using a compatible interface, then granting remote access to our expert technicians, who will guide you through the coding process step-by-step, ensuring a safe and successful outcome.
3. How much does remote coding support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN cost?
The cost of remote coding support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN varies depending on the complexity of the coding task and the vehicle model. Contact us for a personalized quote based on your specific needs.
4. What types of vehicles and features does CAR-CODING.EDU.VN support for remote coding?
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN supports a wide range of vehicles and features for remote coding, including BMW, Volkswagen, Audi, Seat, and Skoda models, as well as various coding tasks such as activating hidden features, clearing fault codes, and programming ECUs.
5. What equipment is required on my end to receive remote coding support?
To receive remote coding support, you’ll need a computer with a stable internet connection, a compatible INPA VCDS interface, and the necessary diagnostic software. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN can provide guidance on selecting the right equipment for your vehicle and coding needs.
6. What happens if something goes wrong during the coding process?
In the event of any issues during the coding process, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN’s expert technicians will provide immediate support to troubleshoot the problem and ensure a safe resolution. We take every precaution to minimize the risk of errors and ensure a successful outcome.
7. Can I activate hidden features on my car using remote coding support?
Yes, remote coding support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN allows you to activate hidden features on your car, such as comfort access, enhanced Bluetooth functionality, and customized lighting options.
8. Is remote coding support available for all car models and years?
Remote coding support is available for a wide range of car models and years, but compatibility may vary. Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN to confirm whether your vehicle is supported and to discuss your specific coding needs.
9. How long does a typical remote coding session take?
A typical remote coding session can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the complexity of the coding task and the vehicle model. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN will provide an estimated timeframe before the session begins.
10. What are the benefits of choosing CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for remote coding support?
Choosing CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for remote coding support offers numerous benefits, including expert guidance, safe and reliable procedures, personalized solutions, and convenient remote access. Our experienced technicians are dedicated to providing the highest level of support and ensuring a successful outcome for every coding task.
Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for expert remote coding support and guidance. Our office is located at 100 Tech Innovation Dr, Suite 500, San Jose, CA 95110, United States.