Are you struggling to diagnose a hard start issue in your TDI engine and need to check the fuel actual vs requested using VCDS? CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers expert remote assistance to help technicians and car enthusiasts accurately diagnose fuel-related problems and optimize engine performance. We provide real-time guidance, ensuring safe and effective coding and diagnostics. Our services include ECU programming, hidden feature activation, and comprehensive technical support, all remotely accessible.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the TDI Fuel System and VCDS Diagnostics
- 1.1 Why is Fuel Actual vs Requested Important in TDI Engines?
- 1.2 What is VCDS and How Does It Help with TDI Diagnostics?
- 1.3 Key Components of the TDI Fuel System
- 1.4 Common Symptoms of Fuel System Issues in TDI Engines
- 2. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Fuel Actual vs Requested with VCDS
- 2.1 Connecting VCDS to Your Vehicle
- 2.2 Navigating to Measuring Blocks or Advanced Measuring Values
- 2.3 Identifying the Correct Measuring Blocks for Fuel Data
- 2.4 Interpreting the Data: What to Look For
- 2.5 Recording and Analyzing Data Logs
- 3. Common Causes of Discrepancies Between Fuel Actual and Requested
- 3.1 Injector Issues: Leaks, Clogging, and Malfunctions
- 3.2 Fuel Pump Problems: Insufficient Pressure and Flow
- 3.3 Fuel Pressure Regulator Failure: Over or Under Pressurization
- 3.4 Sensor Issues: MAF, MAP, and O2 Sensors
- 3.5 Fuel Filter and Line Blockages
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques with VCDS
- 4.1 Performing Injector Balance Tests
- 4.2 Checking Fuel Rail Pressure Sensors
- 4.3 Using Output Tests to Activate Fuel System Components
- 4.4 Diagnosing Hard Starting Issues with VCDS
- 5. Real-World Case Studies and Examples
- 5.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Leaking Injector
- 5.2 Case Study 2: Identifying a Failing Fuel Pump
- 5.3 Case Study 3: Resolving a MAF Sensor Issue
- 6. When to Seek Professional Help from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN
- 7. The Benefits of Remote Car Coding and Diagnostics with CAR-CODING.EDU.VN
- 7.1 Expert Support at Your Fingertips
- 7.2 Save Time and Money
- 7.3 Safe and Secure Coding
- 7.4 Comprehensive Services
- 8. Maintaining Your TDI Fuel System for Optimal Performance
- 8.1 Regular Fuel Filter Replacement
- 8.2 Using High-Quality Fuel
- 8.3 Performing Regular Injector Cleaning
- 8.4 Monitoring Fuel System Parameters with VCDS
- 9. FAQ: Troubleshooting TDI Fuel Issues with VCDS
- 10. Conclusion: Empowering Your TDI Diagnostics with VCDS and Expert Support
1. Understanding the TDI Fuel System and VCDS Diagnostics
1.1 Why is Fuel Actual vs Requested Important in TDI Engines?
Monitoring the fuel actual vs requested in a TDI (Turbocharged Direct Injection) engine is critical for diagnosing various performance issues. The ECU (Engine Control Unit) constantly calculates the amount of fuel needed for optimal combustion based on sensor inputs such as engine load, RPM, and temperature.
- Fuel Actual: The actual amount of fuel being injected into the cylinders, as measured by sensors.
- Fuel Requested: The amount of fuel the ECU is calling for based on various parameters.
A significant discrepancy between these two values can indicate problems such as faulty injectors, a failing fuel pump, or issues with the fuel pressure regulator. By using VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System), you can monitor these values in real-time to pinpoint the root cause of engine performance issues. This process is essential for maintaining optimal fuel efficiency and engine health.
1.2 What is VCDS and How Does It Help with TDI Diagnostics?
VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System) is a software and hardware tool developed by Ross-Tech for diagnosing and coding Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles. It allows you to:
- Read and Clear Fault Codes: Identify and resolve issues stored in the ECU.
- View Live Data: Monitor various engine parameters in real-time.
- Perform Output Tests: Activate components to test their functionality.
- Perform Coding and Adaptations: Modify ECU settings to enable or disable features.
VCDS is an invaluable tool for any technician or car enthusiast working on TDI engines.
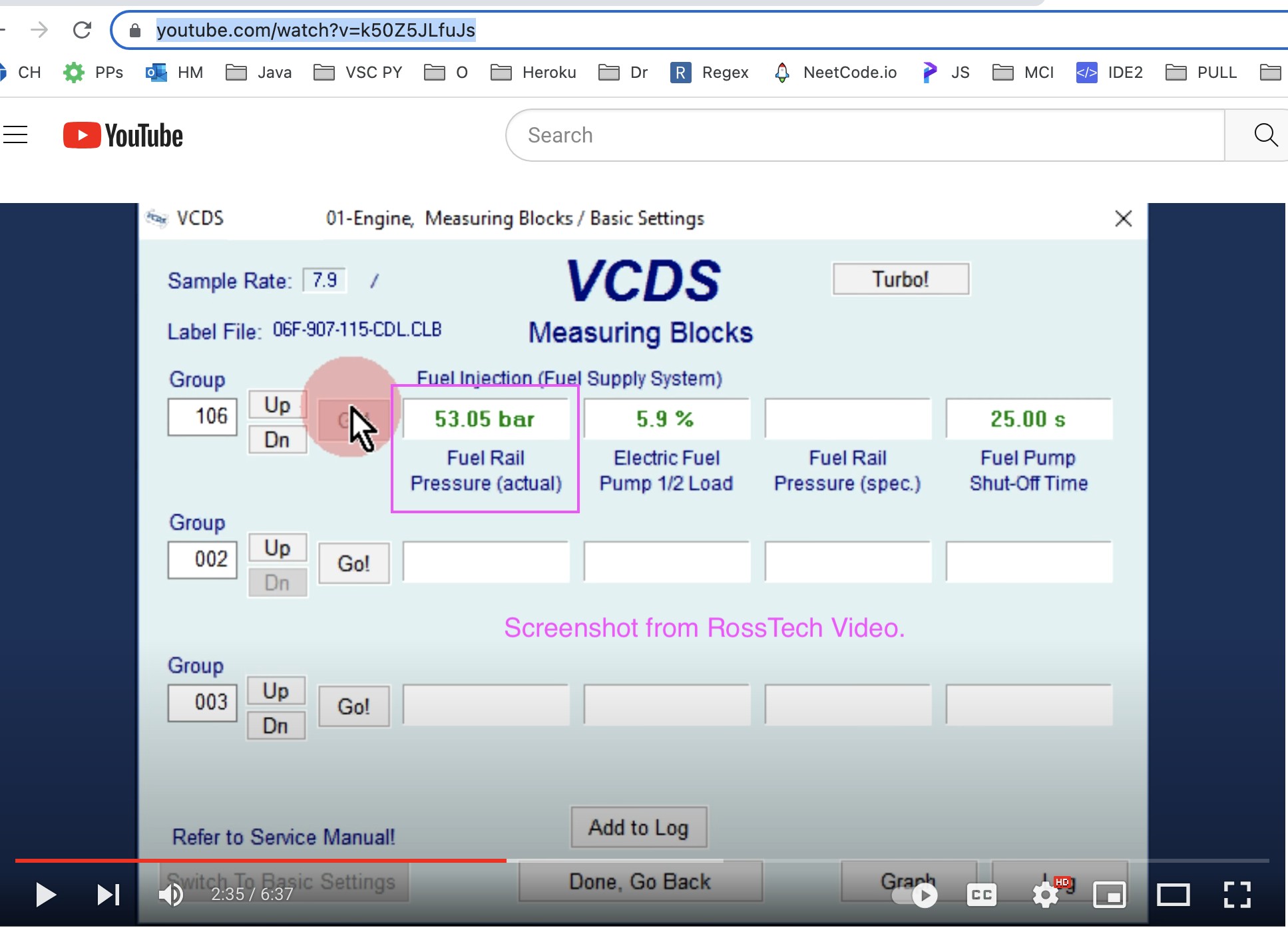 VCDS Interface Showing Measuring Blocks
VCDS Interface Showing Measuring Blocks
1.3 Key Components of the TDI Fuel System
To effectively diagnose fuel-related issues, it’s important to understand the key components of the TDI fuel system:
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel.
- Fuel Pump: Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Removes contaminants from the fuel.
- Fuel Rail: Distributes fuel to the injectors.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator: Maintains consistent fuel pressure in the rail.
- Injectors: Spray fuel into the cylinders for combustion.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): Controls the entire fuel injection process based on sensor inputs.
1.4 Common Symptoms of Fuel System Issues in TDI Engines
Recognizing the symptoms of fuel system issues is the first step in effective diagnosis. Common symptoms include:
- Hard Starting: Engine takes longer than usual to start.
- Rough Idling: Unstable engine RPMs when idling.
- Loss of Power: Reduced engine performance during acceleration.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Decreased MPG.
- Stalling: Engine shuts off unexpectedly.
- Check Engine Light: Illumination of the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL).
- Smoke from Exhaust: Excessive black or white smoke.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Fuel Actual vs Requested with VCDS
2.1 Connecting VCDS to Your Vehicle
- Connect the VCDS Interface: Plug the VCDS interface cable into the OBD-II port of your vehicle. The OBD-II port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Launch VCDS Software: Open the VCDS software on your computer.
- Select Control Module: In VCDS, select “Select Control Module” from the main menu.
- Choose Engine (01): Select “01-Engine” to access the engine control module.
- Verify Connection: Ensure that VCDS has successfully connected to the ECU by verifying the vehicle and ECU information displayed on the screen.
2.2 Navigating to Measuring Blocks or Advanced Measuring Values
Once connected to the engine control module, you need to navigate to the appropriate section to view live data.
- Measuring Blocks (Older ECUs):
- Click on “Measuring Blocks – 08”.
- Enter the group number(s) that contain the fuel actual and requested values. (See Section 2.3 for specific group numbers).
- Advanced Measuring Values (Newer ECUs):
- Click on “Advanced Measuring Values – 08”.
- Select the specific parameters for fuel actual and fuel requested from the list.
2.3 Identifying the Correct Measuring Blocks for Fuel Data
Finding the correct measuring blocks can sometimes be challenging, as they vary depending on the specific ECU and engine code. Here are some common measuring blocks to check for fuel actual and requested values:
- Group 001: Often contains basic engine parameters, including fuel injection quantity.
- Group 004: May include injection timing and fuel quantity data.
- Group 015: Sometimes shows fuel consumption and related values.
- Group 106: As shown in the Ross-Tech video, this group should display fuel rail pressure, but this may not be the case for all TDI models.
- Group 140: Commonly used for monitoring fuel pressure and injector deviations.
- Group 141: May show absolute pressure readings, but without specific identification of what is being measured.
- Group 230: Often used for injector balance and fuel correction values.
If you cannot find the fuel actual and requested values in these groups, try using the “Advanced Measuring Values” option and search for terms like “fuel quantity,” “injection quantity,” or “fuel pressure.”
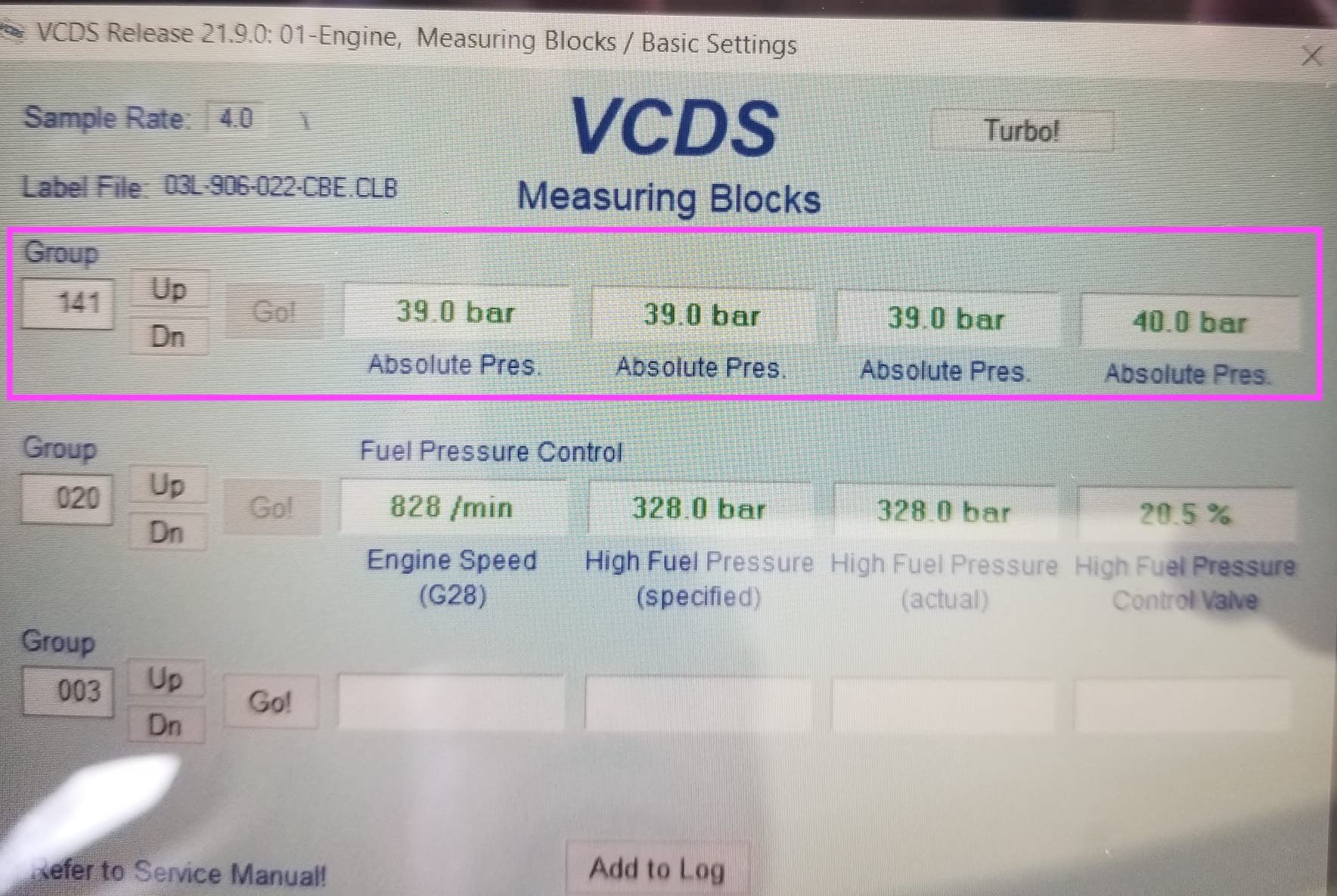 Screenshot of VCDS Measuring Blocks
Screenshot of VCDS Measuring Blocks
2.4 Interpreting the Data: What to Look For
Once you have located the fuel actual and requested values, it’s important to understand how to interpret the data.
- Ideal Scenario: The fuel actual value should closely match the fuel requested value. Minor deviations are normal, but significant differences indicate a problem.
- High Fuel Actual: If the fuel actual is consistently higher than the fuel requested, this could indicate:
- Leaking Injector: An injector is delivering too much fuel.
- Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator: The fuel pressure is too high.
- Sensor Malfunction: A sensor is providing incorrect data to the ECU, causing it to request less fuel than needed.
- Low Fuel Actual: If the fuel actual is consistently lower than the fuel requested, this could indicate:
- Clogged Fuel Filter: Restricting fuel flow to the engine.
- Failing Fuel Pump: Not delivering enough fuel to the rail.
- Injector Clogging: An injector is not delivering enough fuel.
- Fuel Leak: Fuel is leaking from the system before reaching the injectors.
2.5 Recording and Analyzing Data Logs
VCDS allows you to record data logs, which can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues or capturing data during specific driving conditions.
- Start Logging: In VCDS, click on “Log”.
- Select Parameters: Choose the fuel actual, fuel requested, and any other relevant parameters (e.g., engine RPM, engine load, fuel pressure).
- Start Recording: Begin driving or performing the test while VCDS records the data.
- Stop Logging: Stop the logging process once you have captured enough data.
- Analyze the Data: Review the data log in VCDS or export it to a spreadsheet program for further analysis. Look for patterns or anomalies that could indicate a problem.
3. Common Causes of Discrepancies Between Fuel Actual and Requested
3.1 Injector Issues: Leaks, Clogging, and Malfunctions
Injectors are critical components of the fuel system, and any issues with them can cause significant discrepancies between fuel actual and requested.
- Leaking Injectors: Injectors that leak can deliver too much fuel into the cylinders, even when the ECU is requesting less. This can lead to a rich fuel mixture, poor fuel economy, and rough running.
- Clogged Injectors: Injectors that are partially clogged can restrict fuel flow, resulting in too little fuel being delivered. This can cause a lean fuel mixture, loss of power, and hard starting.
- Injector Malfunctions: Electrical or mechanical issues within the injector can also cause it to deliver the wrong amount of fuel. VCDS can often detect injector malfunctions through injector deviation readings.
3.2 Fuel Pump Problems: Insufficient Pressure and Flow
The fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. If the fuel pump is not functioning correctly, it can cause a variety of fuel-related issues.
- Insufficient Pressure: A weak or failing fuel pump may not be able to maintain the correct fuel pressure in the rail. This can result in too little fuel being delivered to the injectors, especially under high load conditions.
- Reduced Flow: A partially clogged fuel pump or a failing pump motor can reduce the overall fuel flow to the engine. This can cause similar symptoms to low fuel pressure.
3.3 Fuel Pressure Regulator Failure: Over or Under Pressurization
The fuel pressure regulator maintains a consistent fuel pressure in the fuel rail. If the regulator fails, it can cause either over-pressurization or under-pressurization of the fuel system.
- Over-Pressurization: If the regulator allows too much fuel pressure, the injectors will deliver more fuel than requested, leading to a rich fuel mixture and potential engine damage.
- Under-Pressurization: If the regulator allows too little fuel pressure, the injectors will not deliver enough fuel, resulting in a lean fuel mixture and performance issues.
3.4 Sensor Issues: MAF, MAP, and O2 Sensors
Sensor malfunctions can provide incorrect data to the ECU, causing it to miscalculate the fuel requirements.
- MAF (Mass Air Flow) Sensor: Measures the amount of air entering the engine. A faulty MAF sensor can cause the ECU to inject too much or too little fuel.
- MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) Sensor: Measures the pressure in the intake manifold. A bad MAP sensor can also lead to incorrect fuel calculations.
- O2 (Oxygen) Sensors: Measure the oxygen content in the exhaust. Faulty O2 sensors can provide incorrect feedback to the ECU, causing it to adjust the fuel mixture inappropriately.
3.5 Fuel Filter and Line Blockages
A clogged fuel filter or blocked fuel lines can restrict fuel flow to the engine, causing a lean fuel mixture and performance issues. Regularly replacing the fuel filter and inspecting the fuel lines for blockages is essential for maintaining optimal fuel system performance.
 Fuel Filter
Fuel Filter
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques with VCDS
4.1 Performing Injector Balance Tests
VCDS allows you to perform injector balance tests, which can help identify faulty injectors. This test measures the fuel correction values for each injector. High correction values indicate that the ECU is trying to compensate for an injector that is not delivering the correct amount of fuel.
- Access Injector Balance Test: In VCDS, go to “01-Engine” and then “Measuring Blocks – 08”.
- Enter Group 013 or 072: These groups typically contain the injector correction values.
- Interpret the Data: The values represent the amount of fuel being added or subtracted by the ECU to balance the fuel delivery. Values close to zero are ideal. Values exceeding +/- 2.0 mg/stroke often indicate a problem.
4.2 Checking Fuel Rail Pressure Sensors
Monitoring the fuel rail pressure sensor can help identify issues with the fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, or fuel leaks. VCDS allows you to view the fuel rail pressure in real-time.
- Access Fuel Rail Pressure Data: In VCDS, go to “01-Engine” and then “Advanced Measuring Values – 08”.
- Select Fuel Rail Pressure: Choose the “Fuel Rail Pressure” parameter from the list.
- Monitor the Data: Observe the fuel rail pressure readings at idle and under load. Compare the actual pressure to the specified values for your vehicle.
4.3 Using Output Tests to Activate Fuel System Components
VCDS output tests allow you to activate various fuel system components, such as the fuel pump or injectors, to test their functionality.
- Access Output Tests: In VCDS, go to “01-Engine” and then “Output Tests – 03”.
- Select Component: Choose the fuel system component you want to test.
- Run the Test: Follow the on-screen instructions to activate the component.
- Observe Results: Monitor the component’s behavior and check for any abnormalities.
4.4 Diagnosing Hard Starting Issues with VCDS
Hard starting is a common symptom of fuel system problems in TDI engines. VCDS can help you diagnose the root cause of hard starting by monitoring various parameters during the starting process.
- Monitor Fuel Pressure: Check the fuel rail pressure during cranking to ensure it reaches the specified value quickly.
- Check Injector Activation: Verify that the injectors are being activated during cranking.
- Look for Fault Codes: Scan for any fault codes related to the fuel system or engine control.
5. Real-World Case Studies and Examples
5.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Leaking Injector
A 2014 VW Passat TDI was experiencing rough idling and poor fuel economy. Using VCDS, the technician monitored the injector correction values and found that one injector had a high positive correction value (+3.0 mg/stroke). This indicated that the ECU was adding extra fuel to compensate for a lean condition in that cylinder. Further inspection revealed that the injector was leaking, causing too much fuel to be delivered. Replacing the faulty injector resolved the issue.
5.2 Case Study 2: Identifying a Failing Fuel Pump
A 2012 Audi A3 TDI was having trouble starting, especially when the fuel tank was low. Using VCDS, the technician monitored the fuel rail pressure during cranking and found that it was not reaching the specified value. Further testing revealed that the fuel pump was weak and unable to deliver enough fuel to the rail. Replacing the fuel pump resolved the starting issue.
5.3 Case Study 3: Resolving a MAF Sensor Issue
A 2015 Skoda Octavia TDI was experiencing a loss of power and poor fuel economy. Using VCDS, the technician monitored the MAF sensor readings and found that they were inconsistent and inaccurate. Replacing the faulty MAF sensor restored the engine’s performance and fuel economy.
6. When to Seek Professional Help from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN
While VCDS is a powerful tool, diagnosing complex fuel system issues can be challenging. If you are unsure about how to interpret the data or are unable to resolve the problem on your own, it’s best to seek professional help.
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers expert remote assistance for TDI diagnostics and coding. Our experienced technicians can:
- Provide Real-Time Guidance: Help you navigate VCDS and interpret the data.
- Perform Remote Diagnostics: Access your vehicle remotely to diagnose the problem.
- Offer Coding and Programming Services: Correct ECU settings and perform necessary adaptations.
- Ensure Safe and Effective Repairs: Guide you through the repair process to ensure optimal results.
7. The Benefits of Remote Car Coding and Diagnostics with CAR-CODING.EDU.VN
7.1 Expert Support at Your Fingertips
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN provides you with access to experienced technicians who specialize in TDI engines. Our experts can guide you through the diagnostic process and help you identify the root cause of your fuel system issues.
7.2 Save Time and Money
Remote diagnostics can save you time and money by eliminating the need to take your vehicle to a shop. Our technicians can quickly diagnose the problem remotely, allowing you to focus on the necessary repairs.
7.3 Safe and Secure Coding
Coding and programming the ECU can be risky if not done correctly. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN ensures that all coding is performed safely and securely, minimizing the risk of damage to your vehicle.
7.4 Comprehensive Services
From basic diagnostics to advanced coding and programming, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers a full range of services to meet your needs.
8. Maintaining Your TDI Fuel System for Optimal Performance
8.1 Regular Fuel Filter Replacement
Replacing the fuel filter at the recommended intervals is essential for maintaining optimal fuel system performance. A clean fuel filter ensures that the fuel pump can deliver the correct amount of fuel to the injectors without restriction.
8.2 Using High-Quality Fuel
Using high-quality fuel can help prevent injector clogging and other fuel system issues. Avoid using fuel from unknown or unreliable sources.
8.3 Performing Regular Injector Cleaning
Regular injector cleaning can help remove deposits and prevent clogging. You can use fuel additives or professional injector cleaning services to maintain the health of your injectors.
8.4 Monitoring Fuel System Parameters with VCDS
Regularly monitoring fuel system parameters with VCDS can help you detect potential problems early on. Keep an eye on fuel pressure, injector correction values, and other relevant data to identify any anomalies.
9. FAQ: Troubleshooting TDI Fuel Issues with VCDS
9.1 Is it safe to perform coding and adaptations on my TDI engine using VCDS?
Yes, it is generally safe if you follow the correct procedures and have a good understanding of the coding process. However, incorrect coding can cause problems, so it’s always best to seek expert help if you’re unsure. CAR-CODING.EDU.VN offers remote assistance to ensure safe and effective coding.
9.2 What kind of equipment do I need to connect to CAR-CODING.EDU.VN for remote support?
You will need a VCDS interface cable, a laptop with internet access, and the VCDS software installed. Additionally, you may need a remote desktop application like TeamViewer to allow our technicians to access your computer remotely.
9.3 How much does remote car coding and diagnostics cost with CAR-CODING.EDU.VN?
The cost varies depending on the complexity of the issue and the amount of time required. Contact us for a quote based on your specific needs.
9.4 What types of TDI vehicles and features can CAR-CODING.EDU.VN support?
We support a wide range of TDI vehicles and features, including VW, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT models. We can assist with diagnostics, coding, programming, and hidden feature activation.
9.5 What are the typical hidden features that can be activated on a TDI using VCDS?
Common hidden features include:
- Coming Home/Leaving Home Lights
- Cornering Lights
- Gauge Staging (Needle Sweep)
- Seatbelt Warning Deactivation
- Window Operation via Remote
9.6 Can CAR-CODING.EDU.VN help me clear fault codes permanently?
Yes, we can help you clear fault codes. However, it’s important to address the underlying issue that caused the fault code in the first place to prevent it from returning.
9.7 How quickly can I get remote support from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN?
We offer both immediate and scheduled remote support. Contact us via WhatsApp to request immediate assistance, or schedule an appointment for a later time.
9.8 What should I do if VCDS is not connecting to my vehicle?
First, ensure that the VCDS interface cable is properly connected to both your computer and the vehicle’s OBD-II port. Verify that the ignition is turned on and that the VCDS software is correctly installed. If you’re still having trouble, contact our support team for assistance.
9.9 Can CAR-CODING.EDU.VN assist with ECU flashing or remapping for performance tuning?
Yes, we offer ECU flashing and remapping services for performance tuning. However, it’s important to understand the potential risks and legal implications of modifying your vehicle’s ECU.
9.10 How can I ensure the security of my vehicle during remote coding sessions?
CAR-CODING.EDU.VN uses secure remote access methods and takes precautions to protect your vehicle’s data. We recommend that you monitor the coding process and disconnect the remote connection once the session is complete.
10. Conclusion: Empowering Your TDI Diagnostics with VCDS and Expert Support
Using VCDS to monitor fuel actual vs requested is a powerful way to diagnose fuel system issues in TDI engines. By understanding the key components of the fuel system, interpreting the data correctly, and performing advanced diagnostic techniques, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve many common problems.
However, if you encounter challenges or are unsure about how to proceed, CAR-CODING.EDU.VN is here to help. Our expert technicians offer remote assistance to guide you through the diagnostic process, perform coding and programming, and ensure safe and effective repairs. Contact us today to experience the benefits of expert remote car coding and diagnostics.
Ready to take control of your TDI diagnostics? Contact CAR-CODING.EDU.VN now for expert remote support!
Office Address (USA): 100 Tech Innovation Dr, Suite 500, San Jose, CA 95110, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CAR-CODING.EDU.VN
Don’t let fuel system issues hold you back. Get the expert help you need from CAR-CODING.EDU.VN and keep your TDI engine running smoothly.